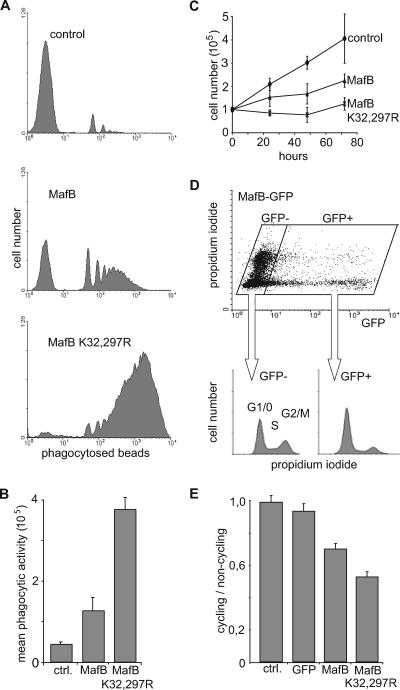
FIG. 4.
Increased functional macrophage differentiation and growth inhibition of myeloid progenitors in the absence of MafB SUMO modification. (A) Representative FACS profiles of E26-ts21 myeloid clones expressing no transgene (control), MafB, or MafB K32,297R mutant after 24 h at 42°C to relieve a E26-ts21-imposed differentiation block and 2 h of incubation with fluorescent PE-conjugated latex beads to monitor phagocytic activity as a measure of functional macrophage differentiation. (B) Quantification of mean phagocytic activity indicating the mean fluorescence intensity as a measure of the number of phagocytosed beads per cell, calculated from FACS profiles as shown in panel A. The average of three independent clones from each genotype is shown. ctrl., control. (C) Growth rate of E26-ts21 myeloid progenitor clones expressing no transgene (control), MafB, or MafB K32,297R mutant. Cell numbers were quantified every 24 h using an MTT assay. (D) QT6 cells were transfected with an expression construct for a MafB-GFP fusion protein and stained with propidium iodide for DNA contents. The cell cycle profiles of GFP-positive (GFP+) and GFP-negative (GFP−) cells were analyzed by propidium iodide staining on fixed cells and plotted separately. (E) The same analysis as in panel D was performed for nontransfected cells (control [ctrl.]) and cells transfected with GFP, MafB-GFP, or MafB K32,297R-GFP. Results are expressed as ratio of cycling (S and G2/M) to noncycling (G1/G0) cells. Error bars in all panels indicate standard errors of the means, and data are representative of at least two independent experiments.