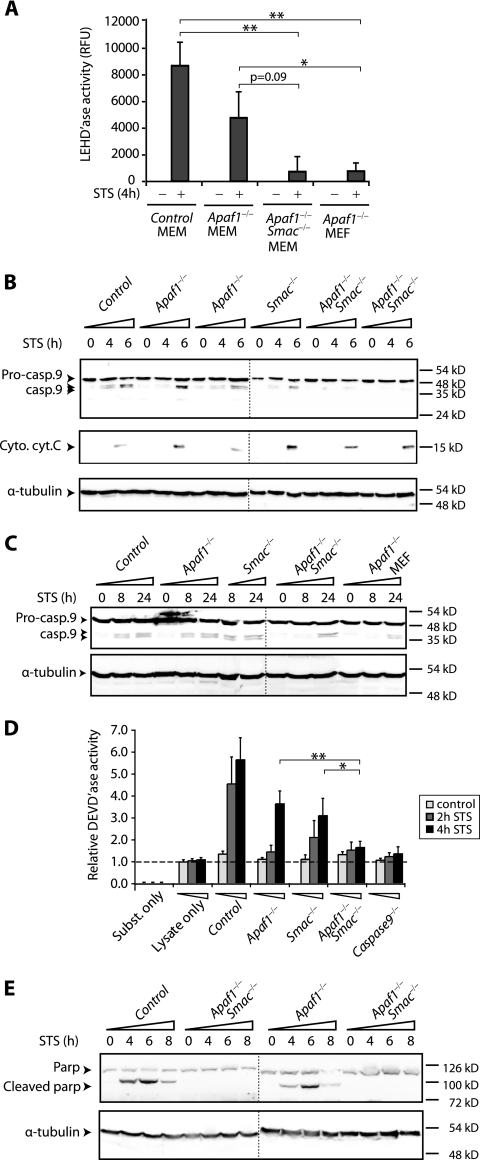
FIG. 4.
Combined loss-of-function mutations in Apaf-1 and Smac inhibit caspase 9 activation and processing in primary myoblasts. (A) Inhibition of caspase 9 enzymatic activity in Apaf-1−/− Smac−/− double mutant myoblasts. Cytosolic fractions from treated or untreated cultures were analyzed for caspase 9 enzymatic activity with the fluorogenic substrate LEHD 4 h post-STS treatment. The bar graphs and standard error bars were calculated from the means of three independent experiments, and the corresponding standard deviations, respectively. * and ** indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.001, respectively, by the Student t test. RFU, •••. (B) Inhibition of caspase 9 processing in Apaf-1−/− Smac−/− double mutant myoblasts. Cultures were exposed to 2 μM STS for the indicated periods; cytosolic fractions were collected and analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody that recognizes both the 49-kDa procaspase 9 (Pro-casp.9) and processed 39- and 37-kDa caspase 9 (Casp.9). Immunoblotting with cytochrome c (Cyto. cyt. C) demonstrates similar kinetics of mitochondrial release in all cultures. α-tubulin served as a loading control. The vertical dotted lines in panels B, C, and E separate two Western blots analyzed in parallel. (C) Similar delays in the kinetics of caspase 9 processing in Apaf-1−/− Smac−/− myoblasts and Apaf-1−/− fibroblasts. Caspase 9 cleavage was analyzed at the indicated time points as for panel B. (D) Inhibition of caspase 3/caspase 7 enzymatic activity, using DEVD substrate in Apaf-1−/− Smac−/− mutant myoblasts. The horizontal dotted line marks the lysate-only controls. (E) Inhibition of PARP cleavage in cytosolic fractions of Apaf-1−/− Smac−/− but not Apaf-1−/− mutant myoblasts following STS treatment.