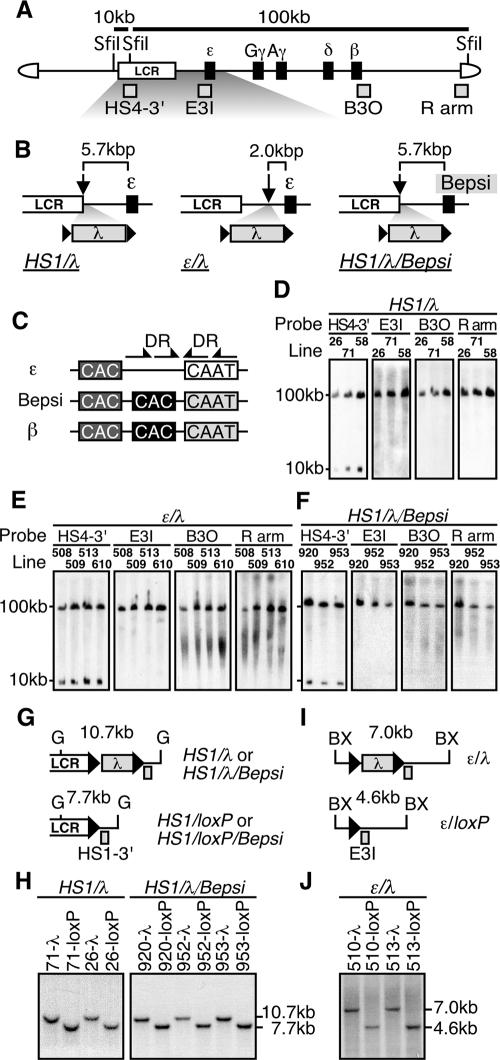
FIG. 2.
(A) Structure of the 150-kbp human β-globin YAC. The positions of the β-like globin genes (solid rectangles) are shown relative to the LCR. SfiI restriction enzyme sites are located 5′ to HS5, between HS4 and HS3, and in the right arm of the YAC. Probes (gray rectangles) used for long-range fragment analyses shown in panels D, E, and F, and expected restriction enzyme fragments with their sizes are shown. (B) Schematic representation of the mutant β-globin loci. The λ DNA fragment (2.3 kbp) was floxed (solid triangles) and inserted 3′ to HS1 (HS1/λ and HS1/λ/Bepsi) or introduced between HS1 and the ɛ-globin gene (ɛ/λ). In the HS1/λ/Bepsi construct, the promoter sequence of the ɛ-globin gene was mutated to mimic that of the β-globin gene, in addition to the λ insertion. (C) The positions of the distal (dark gray) or proximal (solid) CAC boxes are shown relative to the CAAT box in the human ɛ-globin, β-globin, and Bepsi gene promoters. Arrows indicate direct repeat (DR) elements, present only in the ɛ-globin promoter (29). (D, E, and F) Long-range structural analyses of the human β-globin YAC in TgM. The whole β-globin locus is contained within two SfiI fragments (10 and 100 kbp) as described for panel A above. DNAs from thymus cells were digested with SfiI in agarose plugs, separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and hybridized separately to probes (shown in panel A). A schematic representation of the transgene loci around the inserted λ DNA (G and I) and Southern blot analyses for confirming Cre-loxP-mediated in vivo recombination (H and J) are shown. Cre-loxP recombination removes the 2.3-kbp λ DNA insert from each mutated locus, which creates a 7.7-kbp BglII (G, HS1/loxP, and HS1/loxP/Bepsi) or a 4.6-kbp BstXI (BX, ɛ/loxP) fragment in each locus. Tail DNAs from each mutant and loxP footprint TgM lines were digested with BglII (HS1/λ and HS1/λ/Bepsi series) or BstXI (ɛ/λ series), separated on agarose gels, and hybridized to probes HS1-3′ or E3I. Arrowheads, loxP sequences.