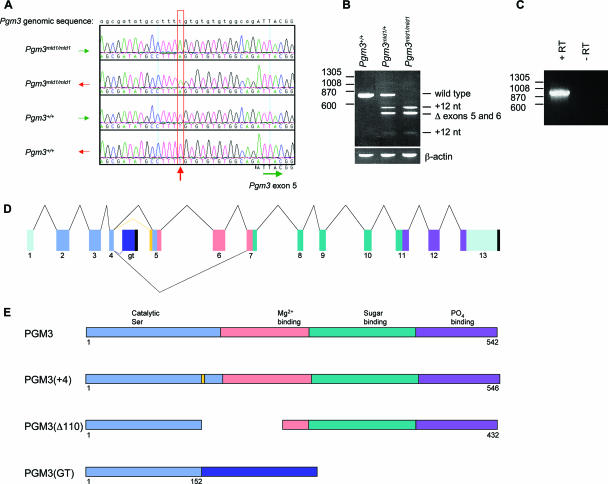
FIG. 1.
The Pgm3mld1 and Pgm3gt alleles of Pgm3 lead to aberrant mRNA splicing. (A) The Pgm3mld1 allele contains a T-to-A transversion 14 bp upstream of exon 5. Electropherograms show the genomic DNA sequences from mice of the indicated genotypes. (B) The Pgm3mld1 allele leads to aberrant mRNA splicing. RT-PCR was performed on splenic cDNA using primers located in exons 1 and 7 of Pgm3. An MslI recognition site is present in the 12-nt insertion; hence, PCR products were digested with MslI to distinguish correct splicing from splicing resulting in the 12-nt insertion. Size (bp) is displayed on the left. (C) Confirmation that the gene trap vector splices into Pgm3 mRNA. cDNA was prepared from W037B08 ES cells, and PCR was performed with the 5′ primer in exon 1 of Pgm3 and the 3′ primer in the gene trap vector. The no-reverse-transcriptase (−RT) control confirms that the PCR product is amplified from mRNA rather than from genomic DNA. (D) Schematic of aberrant mRNA splicing of the Pgm3mld1 and Pgm3gt alleles. Pale green, untranslated region; light blue, domain I; pink, domain II; dark green, domain III; purple, domain IV; dark blue, gene trap insertion; yellow, 12-nt insertion; black, poly(A) site. (E) Mutant proteins encoded by the Pgm3mld1 and Pgm3gt alleles. Light blue, domain I; pink, domain II; dark green, domain III; purple, domain IV; dark blue, gene trap insertion; yellow, 12-nt insertion.