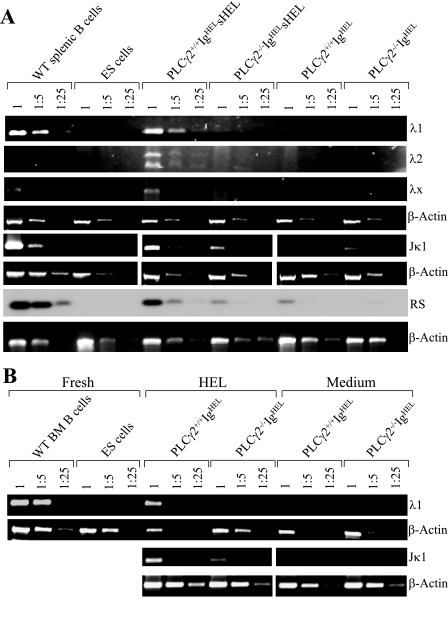
FIG. 5.
Impairment of antigen-induced receptor editing among the endogenous λ and κ loci in PLCγ2-deficient IgHEL B cells. (A) Impairment of antigen-induced receptor editing among the endogenous λ and κ loci in PLCγ2-deficient splenic IgHEL B cells in vivo. Genomic DNA was isolated from the splenocytes derived from wild-type IgHEL, PLCγ2-deficient IgHEL, wild-type IgHEL sHEL, or PLCγ2-deficient IgHEL sHEL mice. Subsequently, the genomic DNA was subjected to a semiquantitative PCR analysis of the β-actin gene; of endogenous λ1, λ2, λx, and Jκ1 rearrangements, and of RS rearrangement. Genomic DNA of splenic B cells from wild-type mice served as a positive control, whereas genomic DNA from ES cells served as a negative control. Data are representative of three independent experiments for λ rearrangements and two independent experiments for Jκ1 and RS rearrangements. (B) Impairment of antigen-induced rearrangements of endogenous λ and κ chain in PLCγ2-deficient BM-derived IgHEL B cells in vitro. BM cells from wild-type or PLCγ2-deficient IgHEL transgenic mice were cultured for 5 days with IL-7 to expand into a B-cell population that expresses the IgHEL BCR. Following further stimulation with (HEL) or without (medium) HEL for 2 days, genomic DNA was isolated from the cells and subsequently subjected to a semiquantitative PCR analysis of the β-actin gene and of endogenous λ1 and Jκ1 rearrangements. Genomic DNA of BM B cells from wild-type mice served as a positive control, whereas genomic DNA from ES cells served as a negative control. Data are representative of three independent experiments for λ rearrangements and two independent experiments for Jκ1 rearrangement. WT, wild type.