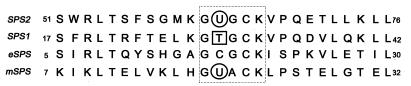
Figure 1.
Partial amino acid sequences of eukaryotic and prokaryotic selenophosphate synthetase. The dashed box indicates the active site glycine-rich region of E. coli selenophosphate synthetase (eSPS). Selenocysteine residues indicated by circled U in mouse SPS2 and M. jannaschii (mSPS) and threonine residue of human SPS1 indicated by squared T occur in place of Cys-17 in eSPS, which is essential for catalytic activity.