Figure 4. CHT immunocytochemistry in the hippocampus and medial septum of P18 rats.
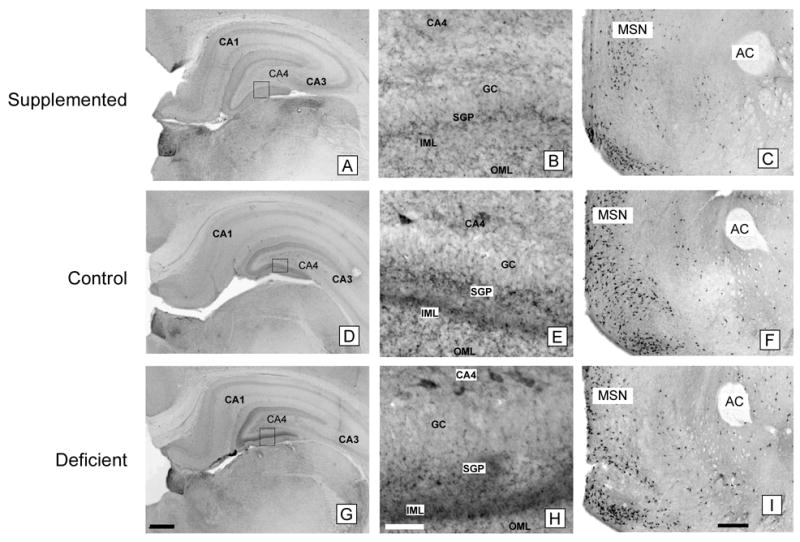
Prenatally choline-supplemented (A, B, C), control (D, E, F), deficient (G, H, I) animals. GC, granular cell layer; SGP, supragranular plexus; IML, inner molecular layer; OML, outer molecular layer; MSN, medial septal nucleus; AC, anterior commissure. The pattern of CHT-immunoreactivity in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus differed among the three groups and CHT-immunoreactive neurons were generally more prominent in CA4 in the deficient group (G, H) and less prominent in the supplemented group (A, B) compared to controls (D, E) despite similar staining intensities in other brain regions such as the medial septal nucleus (C, F, I). Magnification bars: A, D, G - 500 microns; B, E, H - 50 microns; C, F, I - 500 microns.
