Abstract
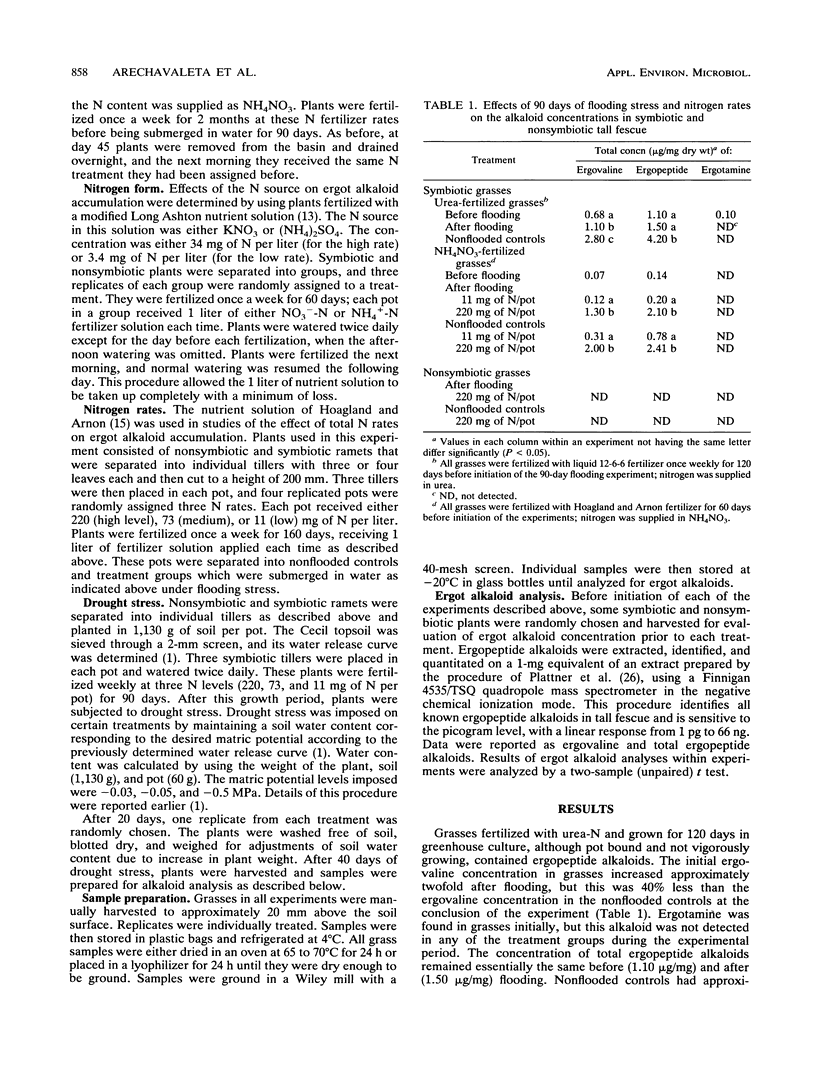
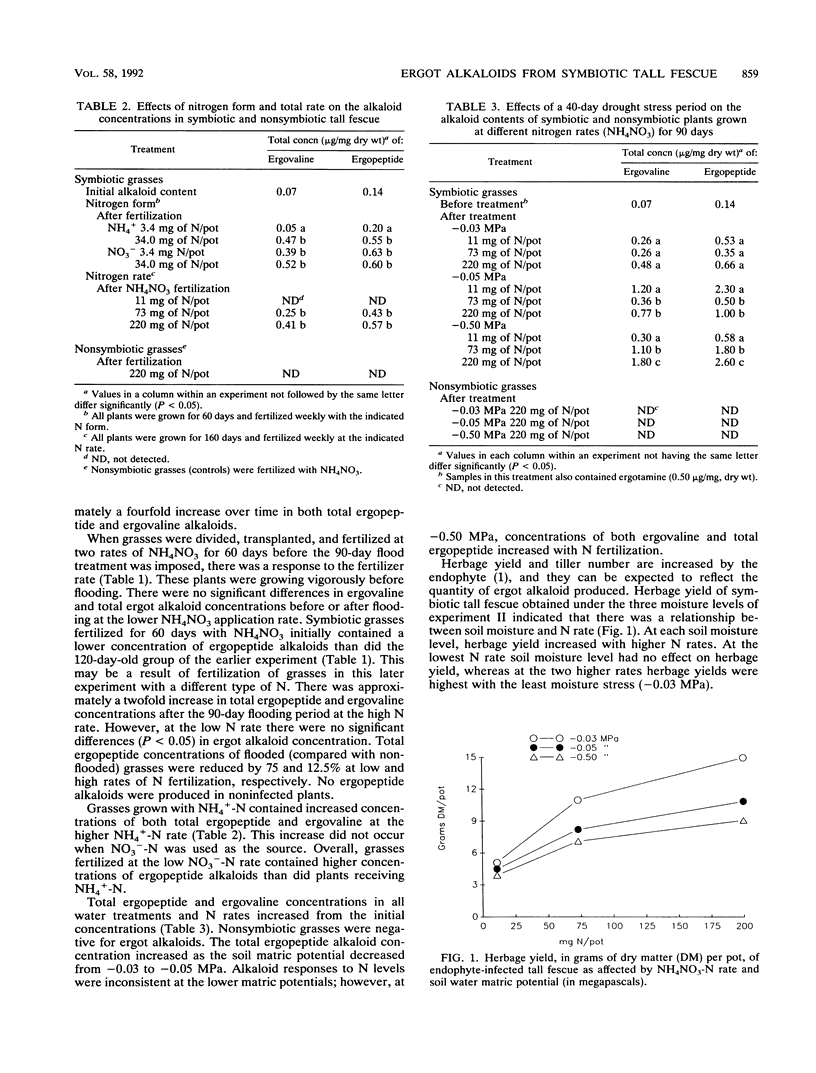
The fungus Acremonium coenophialum is endophytically associated with tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreber). Within this symbiotum the fungus produces ergopeptide alkaloids, which are associated with livestock toxicoses. Environmental effects on the production of ergot alkaloids within the symbiotum are unknown. We conducted a greenhouse study of the effects of flooding, nitrogen rate during fertilization (11, 73, and 220 mg of N per pot weekly), nitrogen form (3.4 and 34 mg of N as NH4+ or NO3- per pot), and drought stress (-0.03, -0.05, and -0.50 MPa) on ergopeptide alkaloid concentrations in one genotype of nonsymbiotic and symbiotic tall fescue grown in plastic pots. It was determined that the concentration of ergovaline, the major type of ergopeptide alkaloid, was increased but was not as high as that in nonflooded controls. Total ergopeptide and ergovaline concentrations in plants receiving high (220 mg of N per pot) and low (11 mg of N per pot) levels of NH4NO3 fertilization were not affected by flooding. The form of nitrogen was important since all concentrations of NO3--N increased ergopeptide alkaloid content, as opposed to the effects of NH4+-N, which was effective only at high concentrations (34 mg of N per pot). Ergopeptide concentrations were highest in drought-stressed plants grown at -0.50 MPa and fertilized at the moderate or high N rate. The results suggest that within this genotype, ergopeptide alkaloid biosynthesis by the fungus is not appreciably affected by flooding but is greatly increased by high rates of N fertilization and moderate water deficit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon C. W., Porter J. K., Robbins J. D., Luttrell E. S. Epichloë typhina from toxic tall fescue grasses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):576–581. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.576-581.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flückiger E., Doepfner W., Markó M., Niederer W. Effects of ergot alkaloids on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. Postgrad Med J. 1976;52SUPPL:57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. C., Dahlman D. L., Siegel M. R., Bush L. P., Latch G. C., Potter D. A., Varney D. R. Insect feeding deterrents in endophyte-infected tall fescue. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):568–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.568-571.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons P. C., Evans J. J., Bacon C. W. Effects of the Fungal Endophyte Acremonium coenophialum on Nitrogen Accumulation and Metabolism in Tall Fescue. Plant Physiol. 1990 Mar;92(3):726–732. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons P. C., Plattner R. D., Bacon C. W. Occurrence of peptide and clavine ergot alkaloids in tall fescue grass. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):487–489. doi: 10.1126/science.3008328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


