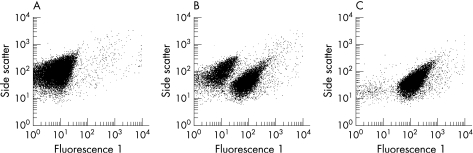
Figure 1 Representative examples of the fluorescence 1 of E. coli ATCC 25922 after incubation with 0.01% acetic acid as vehicle (A) and biopsy extracts from patients with Crohn's disease (B) and ulcerative colitis (C). After cell damage or cell death the membrane potential sensitive dye [bis‐(1,3‐dibutylbarbituric acid) trimethine oxonol] (DiBAC4(3)) enters the bacterial cells, leading to increased fluorescence 1.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.