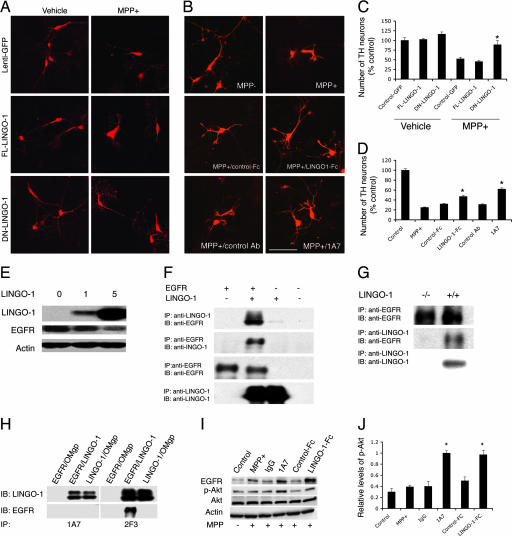
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of LINGO-1 function promotes DA neuronal survival. (A) Cultured VM cells incubated with FL-LINGO-1, DN-LINGO-1, and control lentivirus were treated with 10 μM MPP+ at the fourth day in vitro and fixed at the sixth day in vitro. (B) Cultured VM cells treated with LINGO-1-Fc protein or 1A7 (a LINGO-1-blocking antibody) and control Fc or antibody. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (C) The number of TH neurons was significantly higher in cultures incubated with DN-LINGO-1 than in cultures incubated with FL-LINGO-1 or control vectors after MPP+ treatment (∗, P < 0.01). (D) After exposure to MPP+, the number of TH neurons was higher in LINGO-1-Fc- or 1A7-treated VM cultures compared with cultures treated with vehicle, control Fc, or IgG. ∗, P < 0.05 for LINGO-1-Fc and P < 0.01 for 1A7. (E) COS7 cells were infected with FL-LINGO-1 lentivirus at 0, 1, and 5 multiplicities of infection per cell for 2 days, and EGFR levels were examined. LINGO-1 decreased EGFR expression levels in a dose-dependent manner. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of EGFR and LINGO-1 in cultured cells transfected with LINGO-1 and/or EGFR. (G) Coimmunoprecipitation of EGFR and LINGO-1 in the KO and WT VM tissues. (H) 1A7 blocks binding of LINGO-1 to EGFR in a cotransfected cell line. Transfection of oligodendrocyte–myelin glycoprotein was used as a negative control. (I) Western blots of EGFR, p-Akt, total Akt, and β-actin of VM cultures treated with LINGO-1-Fc or LINGO-1 antibody (1A7). (J) Statistical analysis showed a significant elevation of p-Akt levels in 1A7- and LINGO-1-Fc-treated cultures compared with control antibody and control Fc protein, respectively. Western blots were done at least in duplicate. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation.