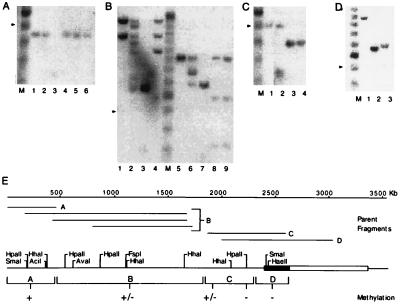
Figure 5.
Analysis of DNA methylation in the insulator region. In each of the panels (A–D), the sensitivity of the parent fragments illustrated in E to digestion by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes is shown. In A, a 454-bp parent fragment was mock-digested (lane 1), digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes HpaII (lane 2), SmaI (lane 4), HhaI (lane 5), and AciI (lane 6), or digested with the methylation-insensitive isoschizomer of HpaII–MspI (lane 3). In lanes 1–4 of B, 1469- and 1219-bp parent fragments were mock-digested (lane 1), digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes HpaII (lane 2) and AvaI (lane 4), or digested with the methylation-insensitive isoschizomer of HpaII–Msp I (lane 3). In lanes 5–9 of B, an 893-bp parent fragment was mock-digested (lane 5), digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes HpaII (lane 6), FspI (lane 8), and HhaI (lane 9), or digested with the methylation-insensitive isoschizomer of HpaII–MspI (lane 3). In C, a 503-bp parent fragment was mock-digested (lane 1), digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes HhaI (lane 2) and HpaII (lane 4), or digested with the methylation-insensitive isoschizomer of HpaII–MspI (lane 3). In D, a 1017-bp parent fragment was mock-digested (lane 1) or digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes SmaI (lane 2) and HaeII (lane 3). In A–D, the arrowhead indicates the position of the 500-bp fragment of the 100-bp ladder in lane M. The results of these experiments are summarized qualitatively in E. +, Full methylation; +/−, partial methylation; and −, absence of detectable methylation. The boxed region delineates the position of the 1.2-kb insulator; stippling indicates the position of the core.