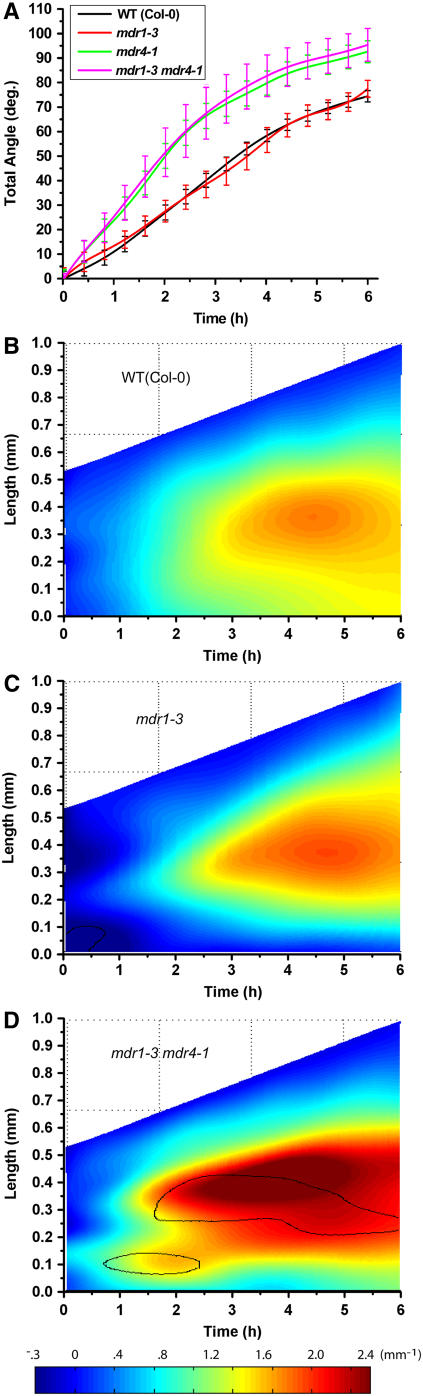
Figure 7.
Characterization of mdr1 mdr4 Gravitropism Using Computational Morphometrics.
(A) Total angle of mdr1 mdr4 (n = 6) roots accruing over time following reorientation ± se displayed the same hypertropic pattern as mdr4 single mutants, and like mdr1-1 and mdr1-2, mdr1-3 (n = 9) was indistinguishable from the wild type.
(B) Spatiotemporal distribution of gravitropic curvature of wild-type (Col) roots, with an average result of 16 individuals.
(C) Spatiotemporal distribution of gravitropic curvature of mdr1-3 roots, with an average of nine individuals.
(D) Spatiotemporal distribution of gravitropic curvature of mdr1-3 mdr4-1 roots, with an average of six individuals. The results demonstrate that mdr1-3 is indistinguishable from the wild type and that the double mutant behaves like mdr4. The black contour line shows where and when curvature is different from the wild type at a significance level of P = 0.05. In all phenotypes, no synergistic effects of the mutations were observed.