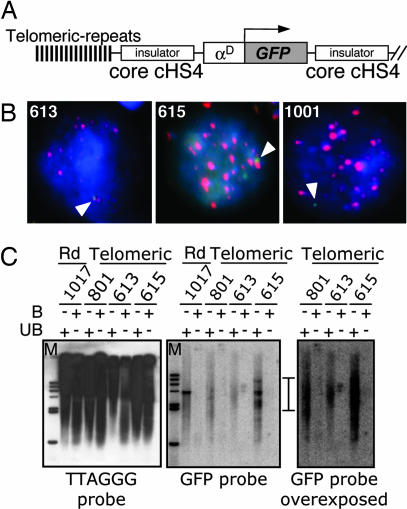
Fig. 2.
Telomeric insertion of insulated and uninsulated transgenes. (A) Transgene vector with the telomeric (TTGAAA)n repeats. (B) Colocalization of transgene with telomeric repeats. In situ hybridization was performed with the clones 613 and 615 and the random integrated clone 1001. Transgene signal was amplified and detected with a FITC-labeled antibody against anti-digoxigenin (green). Telomeric repeats were hybridized with biotinylated oligonucleotides and identified with streptavidin coupled to Alexa Fluor 568 (red). Cells were counterstained with DAPI. Arrows indicate the location of the transgene. (C) Sequence specificity of the purification of telomeres. DraIII-digested HD3 genomic DNA was annealed to telomeric-specific biotinylated oligonucleotides, and telomere–oligonucleotides complexes were captured with streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. The bound DNA was resolved on an agarose gel and probed with a 32P-labeled GFP probe or with an 32P-labeled (TTAGGG)7 oligonucleotide.