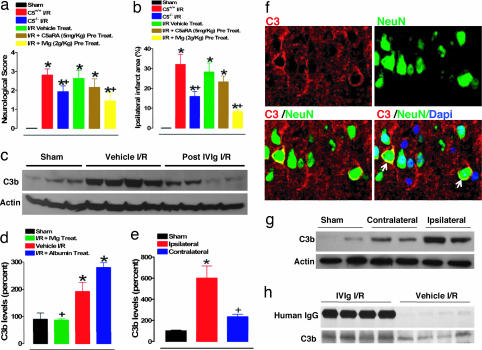
Fig. 3.
Contribution of C5 and C3 complement components to pathophysiology of experimental stroke and attenuation with IVIG. Neurological scores (a) and infarct sizes (b) 24 h after I/R brain injury in wild-type (C5+/+) sham-operated mice (n = 8) and the following groups of mice subjected to I/R stroke: C5+/+ mice (n = 10), C5−/− mice (n = 10), vehicle-treated C5+/+ mice (n = 12), C5a receptor antagonist (C5aRA)-treated C5+/+ mice (n = 8), and IVIG-treated C5+/+ mice (n = 10). C5aRA and IVIG were administered 30 min before onset of ischemia; *, P < 0.001 compared with the sham value; +, P < 0.05 compared with the C5+/+ I/R value. (c) Proteins in cerebral cortex samples from mice subjected to sham surgery (n = 3), vehicle I/R (n = 4), and IVIG-treated at 2 g/kg administered 1 h after stroke (n = 4) were immunoblotted by using anti-C3b and antiactin antibodies. (d) C3b levels determined by densitometric analysis of immunoblots (normalized to actin levels and expressed as a percentage of the mean value for sham-treated mice) in infarcted brain region compared with sham (*, P < 0.01) and vehicle-treated (+, P < 0.01) controls. Quantification of C3b levels (e) and immunoblots (g) in the ischemic area as compared with the corresponding contralateral area; *, P < 0.01 compared with the sham value; +, P < 0.01 compared with the vehicle I/R value. (f) Staining for C3 (red membranous fluorescence), neuronal nuclear marker NeuN (green fluorescence), and double staining including nonneuronal nuclear staining (DAPI) show expression of intrinsic neuronal C3 in the infarcted hemisphere (arrows). (h) Coimmunoprecipitation of human IgG and mouse C3 in the infarcted brain sample.