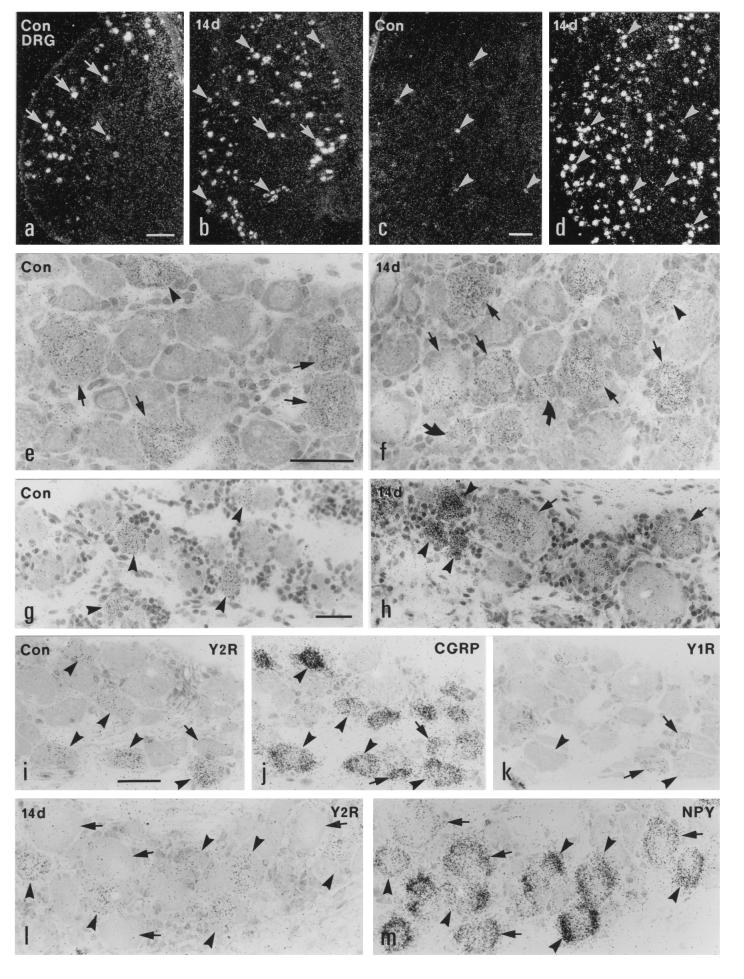
Figure 1.
Dark- (a–d) and bright- (e–m) field micrographs of control (a, c, e, g, and i–k) and ipsilateral (b, d, f, h, l, and m) L5 DRGs of the rat (a, b, e, f, and i–m) and the monkey (c, d, g, and h), hybridized with probes for Y2R (a–i and l), CGRP (j), Y1R (k), and NPY (m) mRNAs, 14 days after unilateral sciatic nerve cut. (a–h) Strong labeling of Y2R mRNA is observed in many large DRG neurons (arrows in a and e) and some medium-sized DRG neurons (arrowheads in a and e) in the normal rat DRGs. After Axo, the number of Y2R mRNA+ neurons is increased in the ipsilateral DRGs of the rat (b). More small (curved arrows), medium-sized (arrowheads), and large (arrows) neurons express Y2R mRNA (b and f). In normal monkey DRGs only a few small neurons express Y2R mRNA (arrowheads in c and g). The number of Y2R mRNA+ small (arrowheads in d and h) and large (arrows in h) neurons is markedly increased in the ipsilateral DRGs of the monkey 14 days after Axo. (i–k) Three 5-μm-thick adjacent sections of a normal rat DRG show that Y2R is expressed in CGRP mRNA+ medium-sized and large (arrowheads) neurons; however, the small neurons expressing Y1R and CGRP do not have Y2R (arrows). (l and m) Two adjacent sections of a ipsilateral rat DRG 14 days after Axo show colocalization of Y2R and NPY mRNAs in many large and medium-sized DRG neurons (arrowheads). There are some NPY mRNA+ large neurons lacking Y1R mRNA (arrows in l and m). (Bars = 200 μm in a–d and 50 μm in e–m.)