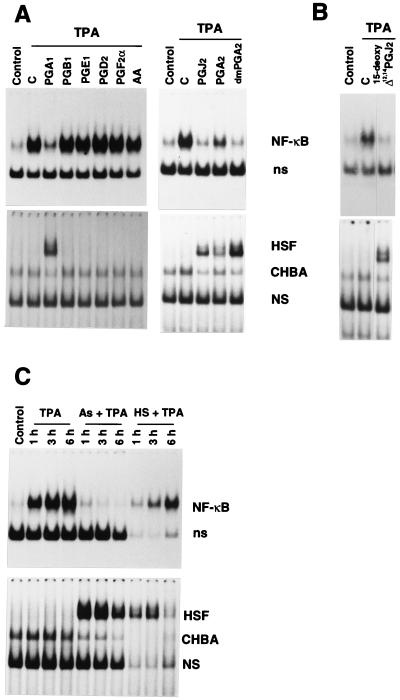
Figure 5.
Effect of AA metabolites and classic HSF inducers on NF-κB activation. (A) Jurkat cells were treated with 24 μM AA, PGA1, PGA2, 16,16-dimethyl-PGA2-methylester (dmPGA2), PGB1, PGD2, PGE1, PGF2α, PGJ2 (Cayman Chemicals) or diluent control (C) for 2 h and then were stimulated with TPA. Control cells were neither stimulated with TPA nor treated with PGs. Whole-cell extracts were prepared 6 h after TPA addition and subjected to EMSA for NF-κB (Upper) or HSF (Lower) activation. Positions of NF-κB and HSF are indicated as in the legend to Fig. 1. (B) Jurkat cells treated for 2 h with 5 μM 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 or control diluent (C) were stimulated with TPA for 3 h, and whole-cell extracts were subjected to EMSA for NF-κB (Upper) or HSF (Lower) activation. (C) Jurkat cells were either treated with 80 μM sodium arsenite (As) (Sigma) or subjected to heat shock at 45°C for 20 min (HS). Two hours after sodium arsenite treatment or heat shock, cells were stimulated with TPA. Control cells were neither stimulated with TPA nor treated with sodium arsenite or heat shock. Whole-cell extracts were prepared at 1, 3, or 6 h after TPA addition and subjected to EMSA for determination of NF-κB (Upper) or HSF (Lower) activation. In the absence of TPA, sodium arsenite and heat shock had no effect on NF-κB activation (data not shown).