Fig. 3.
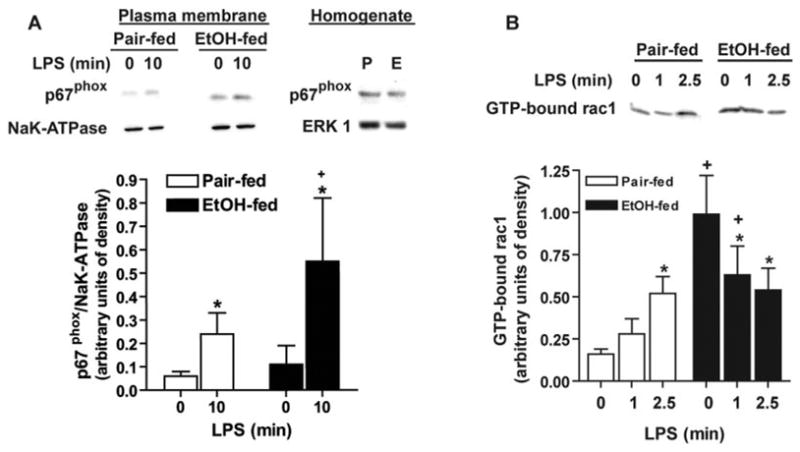
(A) Chronic ethanol feeding increases LPS-stimulated p67phox translocation. Kupffer cells isolated from pair (P)- and ethanol (E)-fed rats were cultured 16–18 h and then stimulated with or without 100 ng/ml LPS for 10 min. Kupffer cells were lysed, and plasma membrane-enriched fractions and homogenates were probed for p67phox by Western blot. NaK-ATPase was used as a control for equal loading of plasma membrane fractions. Values represent means ± sem; n = 5; +, P < 0.05, compared with pair-fed at each time-point; *, P < 0.05, compared with cells not treated with LPS. (B) Chronic ethanol feeding increases guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP)-bound Rac1. Kupffer cells isolated from pair- and ethanol-fed rats were cultured 16–18 h and then stimulated with or without 100 ng/ml LPS for up to 2.5 min. Kupffer cells were lysed, and GTP-bound Rac1 was measured using a Rac1 pull-down assay. Values represent means ± sem; n = 6; +, P < 0.05, compared with pair-fed at each time-point; *, P < 0.05, compared with cells not treated with LPS.
