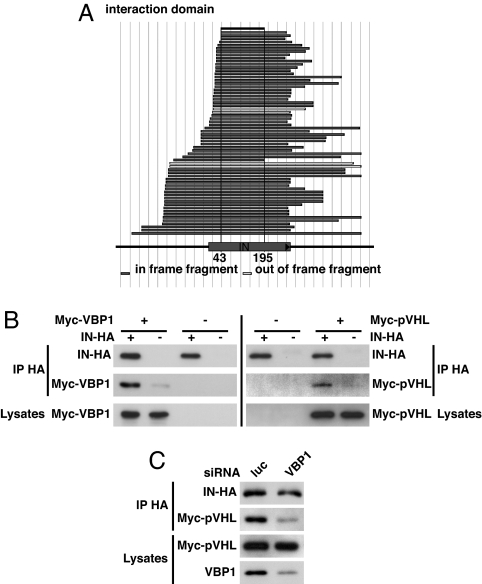
Fig. 1.
VBP1 specifically interacts with HIV-1 IN and mediates IN–pVHL interaction. (A) A yeast two-hybrid screening of a highly complex library of HIV-1 random fragment was performed by using VBP1 as bait. All obtained clones contained the IN gene, and their alignment allows the mapping of a VBP1 interacting domain in IN sequence located between residues 43 and 195. (B) HeLa cells or IN-HA cells (HeLa cells stably expressing IN-HA) were transfected with Myc-VBP1 or Myc-pVHL expression plasmids. Equal amounts of total cellular proteins (lysates) were immunoprecipitated by using anti-HA antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were then analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA or anti-Myc antibody. (C) IN-HA cells were transfected with VBP1-specific (VBP1) or control luciferase (luc)-directed siRNA, prior to transfection with Myc-pVHL expression plasmid. After immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody, immunoprecipitates, as well as endogenous VBP1 and transfected Myc-pVHL in cell lysates, were analyzed by Western blotting by using anti-HA, anti-Myc, or anti-VBP1 antibodies, as indicated. Signals were quantified by densitometric analysis of the scanned autoradiographic films by using ImageJ software and revealed a 69% decrease of the coimmunoprecipitated Myc-pVHL/immunoprecipitated IN-HA ratio in the VBP1 siRNA-treated cells compared with the control cells.