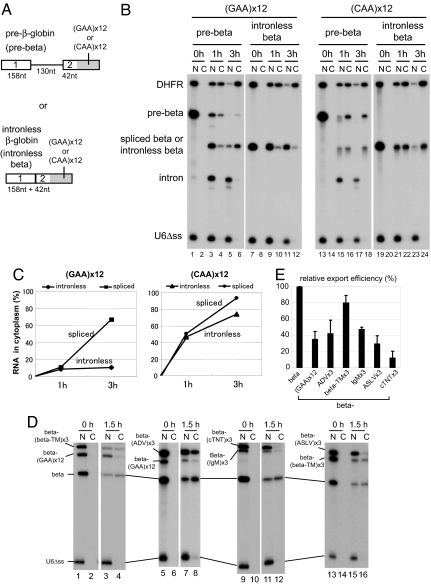
Fig. 4.
Effect of splicing on the nuclear retention by ESEs. (A) Schematic representation of β-globin derivatives. GAA or CAA repeat sequence was fused to either β-globin pre-mRNA (pre-beta; Upper) or intronless β-globin mRNA (intronless beta; Lower). The sizes of the exons and an intron are indicated. (B) 32P-labeled β-globin pre-mRNA (pre-beta) or intronless β-globin mRNA (intronless beta), fused to either GAA (lanes 1–12) or CAA (lanes 13–24) repeat sequence, was injected into the nucleus of Xenopus oocytes, together with 32P-labeled DHFR mRNA and U6Δss RNA. RNA was analyzed immediately (0 h; lanes 1, 2, 7, 8, 13, 14, 19, and 20), 1 h (1 h; lanes 3, 4, 9, 10, 15, 16, 21, and 22), or 3 h (3 h; lanes 5, 6, 11, 12, 17, 18, 23, and 24) after injection. (C) Export kinetics of intronless beta or spliced beta RNA derivatives from B. (D) The same as in Fig. 1 except that an intronless β-globin mRNA instead of U1 was fused to various ESEs and the incubation was 0 or 1.5 h. (E) Quantitation of RNA export from three independent experiments as in D. N, nuclear fractions; C, cytoplasmic fractions.