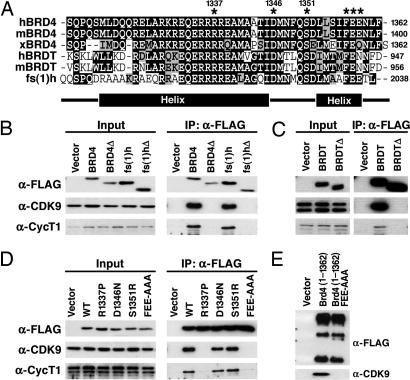
Fig. 2.
A C-terminal peptide conserved among BRD4, BRDT, and fs(1)h mediates P-TEFb interaction. (A) Alignment of the C termini of human, murine, and Xenopus BRD4; human and murine BRDT; and Drosophila fs(1)h. Identical residues are indicated in black, and conserved residues are in gray. The locations of α-helices predicted by computer analysis are indicated below. (B) Vectors encoding the C termini of human BRD4(1209–1362), BRD4(Δ1209–1344), fs(1)h(1885–2038), or fs(1)hΔ(1885–2020) were transfected into 293T cells. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates (IP) were immunoblotted with anti-FLAG, anti-cyclin T1 (anti-CycT1), and anti-CDK9. (C) Expression constructs encoding the C terminus of BRDT (residues 821–956) or a C-terminal deletion mutant [BRDTΔ(821–938)] were transfected into 293T cells. Whole-cell lysates were prepared, and BRDT was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads. (D) C-terminal residues conserved among BRD4, BRDT, and fs(1)h were mutated in FLAG-BRD4(1209–1362) (indicated by an asterisk in A). Plasmids encoding BRD4 point mutants 1209–1362R1337P, D1346N, S1351R, and FEE1357AAA were transfected into 293T cells. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for FLAG, CycT1, and CDK9. (D) Plasmids encoding FLAG tagged wild-type (WT) BRD4 (1–1362) or mutant (1–1362FEE) were transfected into 293T cells. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates were blotted for anti-FLAG and anti-CDK9.