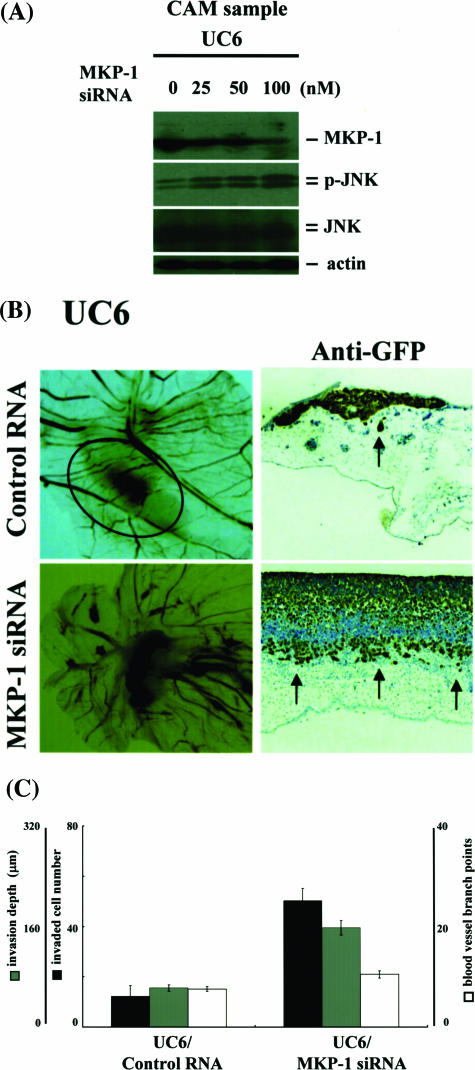
Figure 4.
Reduction of MKP-1 enhances JNK activation and the dependent invasion/angiogenesis in human urothelial carcinoma cells. A: The human urothelial carcinoma cell line UMUC6 was co-transfected with pTK-GFP and MKP-1 siRNA ranging from 0 to 100 nmol/L. After a 24-hour cultivation, cells were seeded on top of CAMs and incubated for 3 days. Grafting tissue samples were collected and lysed with lysis buffer. Knockdown efficacy of MKP-1 and expression of phosphorylated JNK were examined by immunoblotting using anti-MKP-1, anti-phosphorylated JNK, and anti-JNK antibodies. B and C: Cells were transfected with 100 nmol/L of control or MKP-1 siRNA. After a 24-hour cultivation, they were seeded on top of CAMs and incubated for 3 days. Macroscopic (left column) and immunohistochemical findings (right column) using anti-GFP antibodies for cross sections are demonstrated in B. Invasion was assessed by counting the number of invading cells per high-power field and quantifying front depth of invasion (three or more cells), whereas vessels were enumerated by counting vessel branch points in a double-blinded manner. C: Each value is the mean ± SE of at least three experiments.