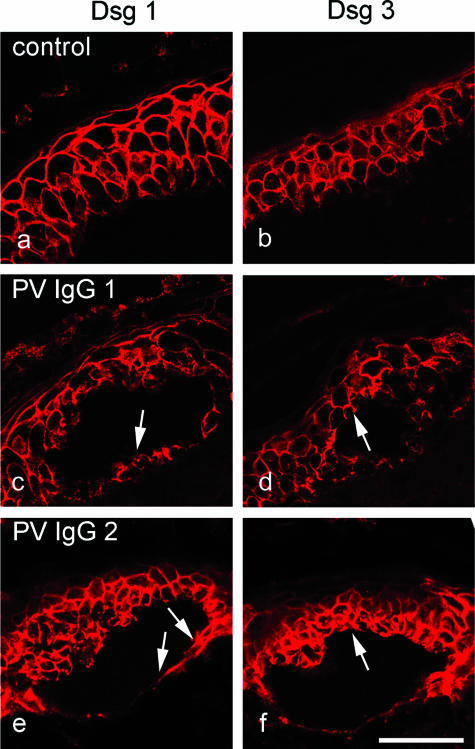
Figure 2.
In cultured intact human epidermis, PV-IgG caused epidermal splitting where both Dsg1 and Dsg3 were present. Skin was immunostained for Dsg 1 (a, c, and e) and Dsg 3 (b, d, and f). In untreated skin, Dsg 1 and Dsg 3 displayed broad overlapping distribution patterns (a and b). Dsg 1 was expressed throughout the epidermis with a decreasing gradient from superficial to basal layers. Despite its basal prominence, Dsg 3 was present in all layers except the upper granular layer. Incubation with PV-IgG containing antibodies against both Dsg 1 and Dsg 3 lead to suprabasal splitting (c–f). Note that Dsg1 was present in the basal layer underneath the split (arrows in c and e) and that Dsg 3 was found above the cleavage plane (arrows in d and f). Bar = 50 μm.