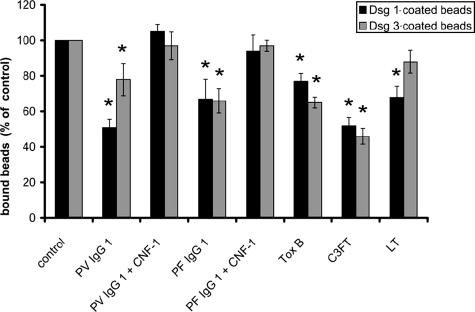
Figure 8.
Pemphigus IgG and inhibition of Rho GTPases reduced desmoglein-mediated adhesion. Adhesion of beads coated with Dsg 1 or Dsg 3 was assayed using laser tweezers. Beads were allowed to settle on the cell surface for 30 minutes before binding was probed (control). After incubation with pemphigus IgG for 120 minutes in the absence or presence of CNF-1 to activate Rho GTPases or after incubation with bacterial toxins for 180 minutes to inhibit Rho GTPases, binding was tested again. Compared with controls, PV-IgG 1 and PF-IgG 1 significantly reduced adhesion of Dsg 1- and Dsg 3-coated beads to the cell surface, which was completely blocked by simultaneous activation of Rho GTPases. Similarly, inhibition of Rho A, Rac 1, and Cdc42 by toxin B as well as specific inhibition of Rho A by C3FT resulted in significant loss of bead binding. Inhibition of Rac 1 by LT caused significant reduction of Dsg 1-mediated binding only. Significance compared with controls is indicated by asterisks (P < 0.05).