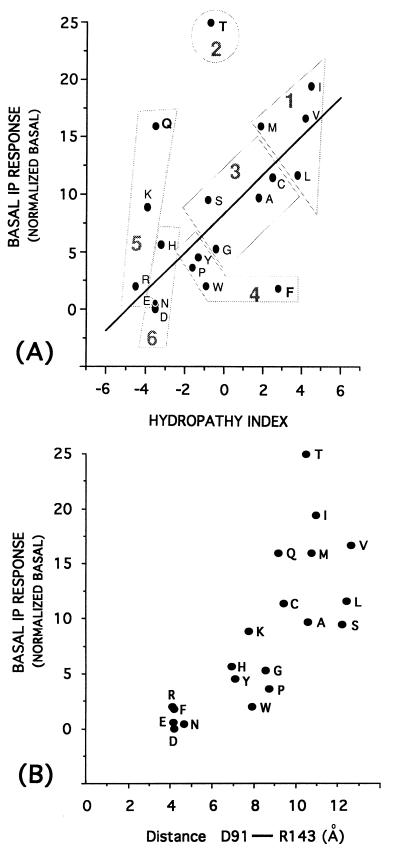
Figure 2.
(A) Correlation between the constitutive activity (basal IP response) of the 19 mutants of D142 and the hydropathy indices of the replaced amino acids. Linear regression equation: Basal IP response = 8.29 (± 0.81) + 1.69 (± 0.27) × hydropathy index; n = 17, r = 0.85, s = 3.2, where n is the number of compounds, r is the correlation coefficient, s is the standard deviation, and the numbers in parentheses are the 95% confidence intervals. The three outliers, F, Q, and T, have been discarded from correlation. The figure also shows the six groups in which the amino acids can be clustered based on the principal component analysis previously described considering 29 of their different experimental properties (22). This analysis identifies three main components, z1, z2, and z3, whose values are regarded as principal properties of the natural amino acids. z1 is mainly related to hydrophilicity, z2 is additionally influenced by size and some hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity scales, and z3 contains information from the analysis of pKa, pI, and 1H-NMR values. (B) Correlation between the constitutive activity (basal IP response) of the 19 mutants of the D142 site and the distance between the γ-C-atom of D91 (TMDII) and the ζ-C-atom of R143 (TMDIII). This distance was measured on the averaged minimized structures of the α1B-AR wild type carrying D142 deprotonated and of the 19 mutants of D142.