Figure 6.
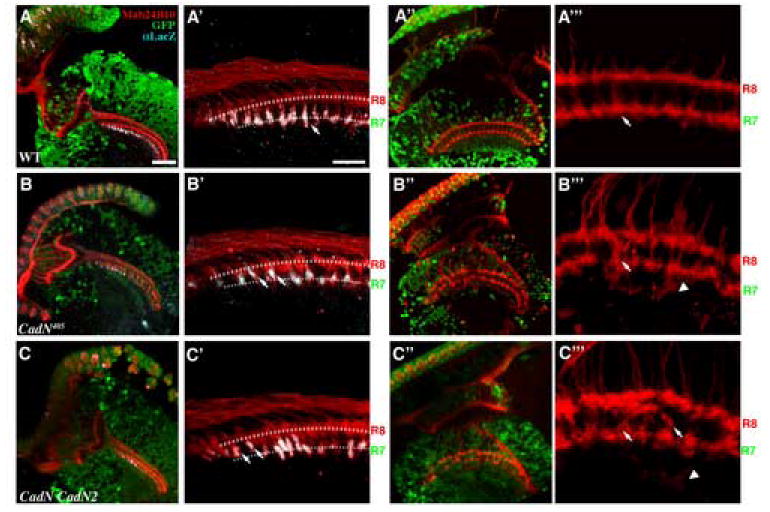
CadN is required in medulla neurons for R7 targeting in the first layer-selection stage. Optic lobes were rendered wild-type (A-A”’), CadN (B-B”’), or CadN CadN2 double mutant (C-C”’) using the ELF system; the mosaic neurons were marked by the loss of GFP signal. (A-C’) The initial projections of R7 axons into the R7-temporary layer were assessed at 17% APF. R7 axons were labeled using PM181-LacZ (grey) and R-cell axons were visualized with MAb24B10 (red). (B, B’ and C, C’) In the CadN or CadN CadN2 target-mosaic animals, genetically wild-type R7 axons projected into the medulla neuropil, composed of processes of mutant medulla neurons. Unlike in wild-type (A-A’), many of the CadN mutant R7s axons (33.7 %) fail to project past R8 growth cones (arrows). (B”, B”’ and C”, C”’) At 37% APF, R7 and R8 axons exhibit severe topographic mapping and layer-specific targeting defects (arrows) in the CadN or CadN CadN2 mutant target-mosaic animals. Moreover, some R-cell axons extend processes to deeper layers (arrowheads). A’-C’ and A”’-C”’ are high magnification view of A-C and A”-C”, respectively. The presumptive R7- and R8-temporary layers are indicated by dotted lines in (A’-C’). Scale bars: in A, 30 μm for B-C and A”-C”; in A’, 10 μm for B’-C’ and A”’-C”’.
