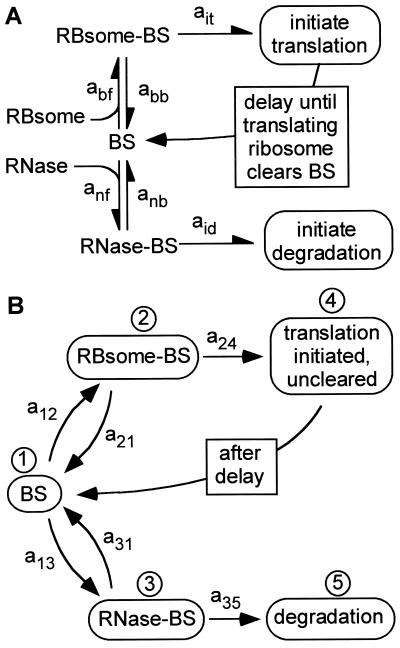
Figure 2.
Reaction model (A) and binding state model (B) characterizing sequential competitions between ribosomes and RNase E at two closely located sites on the transcript (denoted BS for binding sites). Binding of either occludes the binding site of the other. After ribosome binding leading to initiation of translation, the competition recurs after a delay while the translating ribosome’s footprint clears the two sites. This process repeats until RNase E binds and initiates degradation of the transcript. Each competition is an independent event with a probabilistic outcome. A transcript is initially in state 1 and thereafter in one of the five states shown in B. The number of proteins produced, N, will be the number of times state 4 is traversed before the process terminates in state 5. When the system is in any state i, aij dt is the probability of transition to state j in time interval {t, t + dt}, where i and j each denotes one of the states {1, … , 5}. Observations (see text) suggest that a24, a12 ≫ a21 and a35, a13 ≫ a31. When the system is in state 1, the probability of another protein is approximately (a12 a24)/(a12 + a13)(a21 + a24), neglecting higher order transitions such as 1 → 2 → 1 → 2 → 4.