Figure 1.
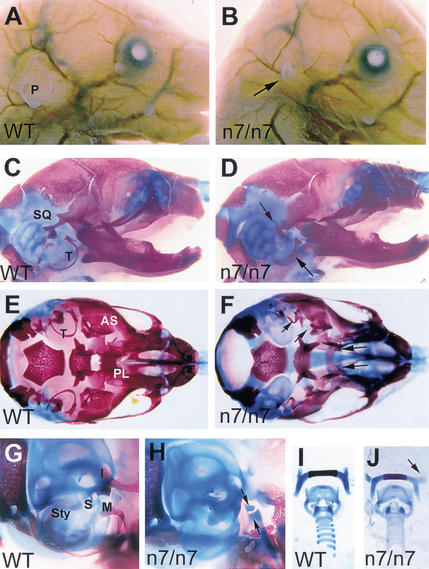
Craniofacial defects in newborn Fgfr1n7/n7 hypomorphic mutants. Side views of newborn wild-type (A) and Fgfr1n7/n7 (B) heads. Arrow in B indicates the pinna of the outer ear, which is significantly reduced in the mutant. Side views of wild-type (C) and Fgfr1n7/n7 (D) skulls. Note the normal size of the skull and mandible of the mutant. The posterior part of the squamosal bone (SQ) fails to form the retrotympanic recess and tympanic rings (T) are reduced or missing in the mutant (arrows in D). Ventral views of wild-type (E) and Fgfr1n7/n7 (F) skulls, after removal of the lower jaw. Alisphenoid bone (AS), palatine (PL), and tympanic ring (T) are indicated in the wild type. The mutant in F has a cleft palate, a malformed posterior part of the alisphenoid bones and reduced tympanic rings (arrows). Side views of wild-type (G) and mutant (H) middle ears. Styloid process (Sty), stapes (S), incus (I), and malleus (M) are indicated in the wild type. The mutant (H) lacks distinguishable middle ear ossicles. The arrows in H point at remaining cartilage condensations at the end of the Meckel's cartilage. Dissected hyoid bone and laryngeal cartilages from wild-type (I) and Fgfr1n7/n7 (J) mice. Note the abnormal orientation of the lesser horns of the hyoid bone in mutant (arrow in J).