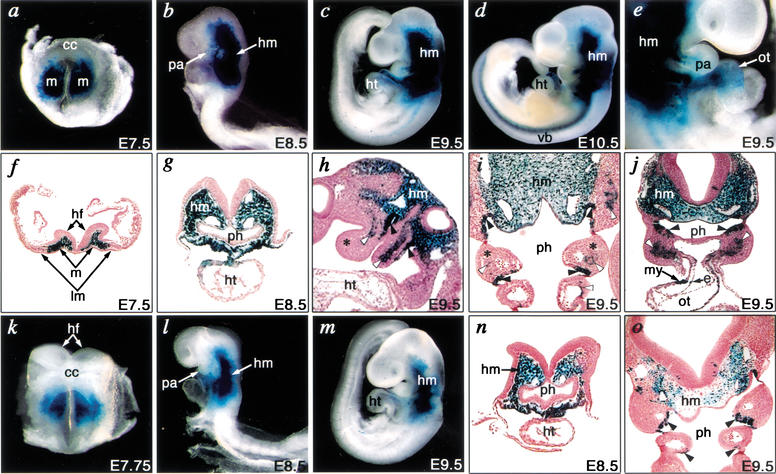
Figure 2.
Developmental regulation of Tbx1 expression by tissue-specific enhancers. Embryos from a stable transgenic line harboring the 12.8-kb fragment (construct 1) were analyzed at various times during mouse embryogenesis. (a–d) Whole-mount photographs of embryos from E7.5 to E10.5. (e) Right lateral view of embryo focusing on the pharyngeal arch and heart at E9.5. (f–j) Transverse (f,g,j), sagittal (h), and frontal (i) sections counterstained by Nuclear Fast Red from E7.5 to E9.5. (a,f) lacZ was expressed in mesoderm cells (m) that give rise to cranial mesenchyme, but not in the cardiac crescent (cc) or lateral plate mesoderm (lm) at E7.5. (b,g) Expression of lacZ was detectable in the head mesenchyme (hm) and pharyngeal arch (pa) at E8.5. (c,h,i,j) lacZ expression was detectable in head mesenchyme, pharyngeal arch mesoderm (white arrowheads), and endoderm (black arrowheads), but not in neural-crest-derived mesenchyme (asterisks) at E9.5. (d) Expression of lacZ extended to the primordia of vertebral bodies (vb). (e,j) lacZ was expressed in both myocardial (my) and endocardial (e) layers of the cardiac outflow tract (ot) at E9.5. (k–m) Whole-mount photographs of embryos from a stable transgenic line harboring the 1.1-kb fragment (construct 6) at E7.75 to E9.5. (n,o) Transverse (n) or frontal (o) sections of l or m, respectively, counterstained by Nuclear Fast Red. (k) lacZ expression in mesoderm cells was observed similar to panel a at E7.75. (l,n) lacZ was detectable in head mesoderm as in b and g, but excluded from the pharyngeal arch at E8.5. (m,o) Expression of lacZ in head mesenchyme and pharyngeal endoderm was detectable similar to c, i, and j, but expression in pharyngeal mesoderm was absent. hf, head fold; ht, heart; ph, pharynx.