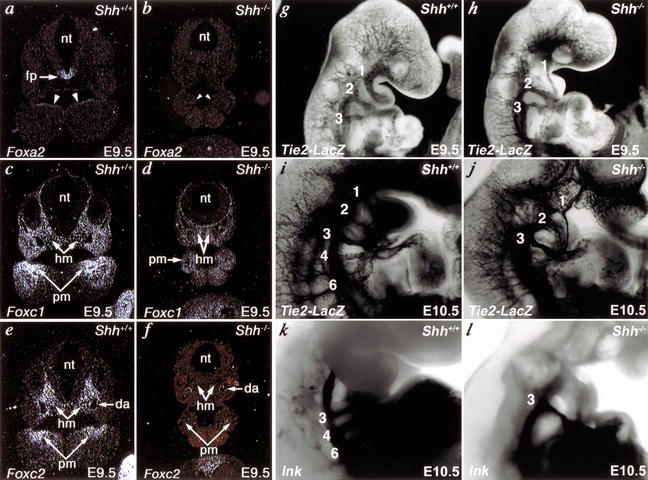
Figure 6.
Shh regulates Fox proteins and aortic arch development. (a,b) Radioactive in situ hybridization on transverse sections of E9.5 mouse embryos shows that Foxa2 is down-regulated in floor plate (fp) of neural tube (nt) and pharyngeal endoderm (arrowheads) of Shh−/− embryos compared with wild-type (Shh+/+) embryos. (c,d) Foxc1 was expressed in the head mesenchyme (hm) and pharyngeal arch mesenchyme (pm) of Shh mutant embryos at relatively low levels compared with wild-type embryos. (e,f) Foxc2 was undetectable in the head mesenchyme and pharyngeal arch mesenchyme of Shh mutant embryos compared with wild-type embryos. Foxc2 expression in dorsal aortae (da) was normal in Shh mutant embryos. a, c, and e are serial sections from a wild-type embryo, and b, d, and f are serial sections from an Shh mutant embryo. (g–l), Aortic arch defects in Shh mutants. lacZ driven by the Tie2 promoter marked the vasculature and revealed a small first aortic arch artery at E9.5 (h) and absence of the fourth and sixth arch arteries at E10.5 (j) compared with wild type (g,i). India ink injection demonstrated similar absence of the fourth and sixth arch arteries. Arch arteries are indicated numerically. Right lateral views are shown with close-ups of the pharyngeal arch region in i–l.