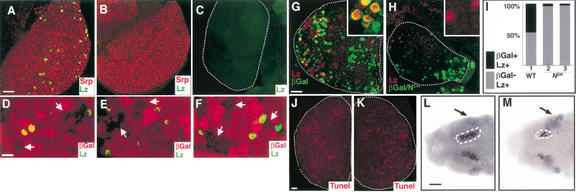
Figure 1.
Notch signaling in hematopoiesis. (A) Wild-type first lymph gland lobe from a third instar larva raised at 29°C and stained with antibodies against Lz (green) and Serpent (red). Lz is expressed in a distinct subset of Srp+ hemocytes. (B) Nts1 raised at 29°C and stained as in A. Lz protein is not expressed, but Srp (red) expression remains unaffected. (C) Su(H)SF8/Su(H)AR9 lymph gland stained with Lz antibody. Lz protein is not expressed. (D–F) hsp70-flp/FRT clones (arrows) of Notch pathway members are marked by the absence of βGal expression (red). Lz expressing cells (green) are excluded from mutant clones of N55e11 (D), Nts1 (E), and Su(H)Δ47 (F). (G) hsp70-flp; Ay-Gal4, UAS-βGal/+. In this control “flp-out” experiment (Ito et al. 1997), βGal-expressing clones were induced in the first larval instar and analyzed in the third instar larval lymph gland. Nuclear βGal (green) marks cells in which Gal4 is expressed. Many examples of colocalization of Lz and βGal can be seen (inset). (H) hsp70-flp; Ay-Gal4, UAS-βGal/UAS-NDN. In this genotype, βGal+ cells (green) also express NDN. Lz (red) and NDN (green) are mutually exclusive (inset), suggesting a requirement for Notch in the development of Lz+ cells. Additionally, the lymph gland size is reduced relative to wild-type controls. (I) Cell counts from the Notch clonal analysis described as in G and H. For wild-type clones (histogram 1), 20 lymph gland lobes were counted and of 1652 total Lz+ cells, 768 were also βGal+. NDN clones were either counted from equivalent number of lymph gland lobes (histogram 2) or equivalent number of Lz+ cells (histogram 3). From 20 lymph gland lobes counted (histogram 2), of 153 total Lz+ cells, 148 did not express βGal and, therefore, NDN. Similarly, of 1370 total Lz+ cells counted from 68 lymph gland lobes (histogram 3), only 55 expressed βGal. In either case, ∼96% of the Lz+ cells did not express βGal. (J) hsp70-flp; Ay-Gal4, UAS-βGal/+. Experimental conditions are the same as in G. Tunel staining (red) marks apoptotic cells. (K) hsp70-flp; Ay-Gal4, UAS-βGal/UAS-NDN. Experimental conditions are the same as in H. Tunel staining (red) is similar to wild type (J). (L) Dorsal view of a wild-type stage 12 embryo. Anterior is to the left. Expression of Lz protein is observed in crystal cell precursors (circled) of the head mesoderm. Additional ectodermal expression of Lz (arrow) is unrelated to its role in hematopoiesis (Lebestky et al. 2000). Cell counts were performed for 30 bilateral clusters of Lz+ cells. (M) Dorsal view of a N55e11 stage 12 embryo. Fewer Lz expressing crystal cell precursors (circled) are seen. In contrast, Lz expression in the ectoderm is expanded (arrow), due to the neurogenic phenotype of Notch, unrelated to its role in hematopoiesis. In C, G–H, and J–K, the dotted line marks the outline of the lymph gland lobe. Bars: A–C,G–H,J–M, 25 μm; D–F, 10 μm.