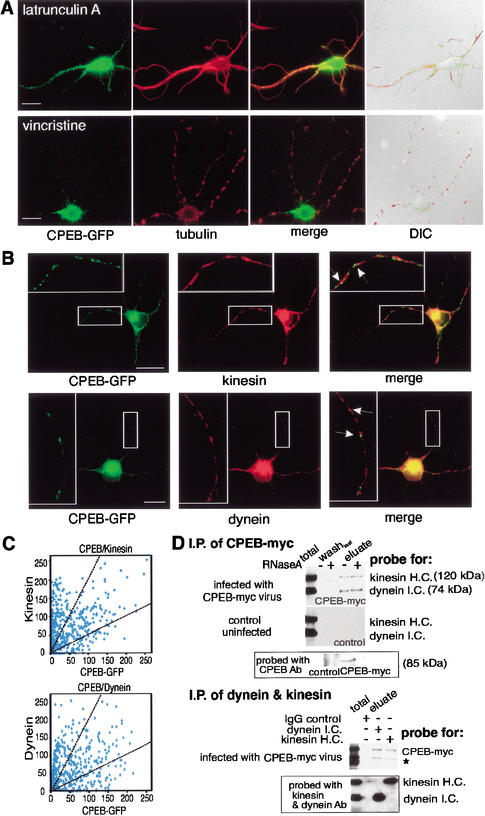
Figure 5.
CPEB-GFP particles contain dynein and kinesin and are transported in a microtubule-dependent manner. (A) CPEB-GFP transfected hippocampal neurons were treated with latrunculin A, which disrupts microfilaments, or vincristine, which disrupts microtubules, and examined for GFP fluorescence (green) as well as tubulin immunofluorescence (red). Only vincristine disrupted most microtubules by leaving a patchwork of these structures, whereas neither treatment affected dendrite integrity (merged DIC image). Vincristine, but not latrunculin A, also inhibited GFP-CPEB transport. (B) CPEB-GFP-expressing neurons were immunostained with kinesin or dynein antibody and imaged by confocal microscopy. The magnified images (insets) show particles containing CPEB-GFP colocalized with motor proteins (solid arrows). (C) The green and red fluorescence intensities representing CPEB-GFP and either kinesin or dynein were analyzed from 407 and 403 dendritic CPEB-GFP-containing particles, respectively. The intensity of kinesin or dynein in each particle was plotted against the intensity of CPEB-GFP in the same particle. The two broken lines define the region in which CPEB and the molecular motors in particles were detected in 1:2 and 2:1 intensity ratios. Bars, 10 μm. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of kinesin and dynein with CPEB-myc13. Cytoplasmic extracts prepared from hippocampal neurons, either uninfected or infected with Sindbis virus-expressing myc-tagged CPEB, were immunoprecipitated with myc antibody in the absence or presence of RNase A. The antibody beads were washed, eluted with 2 M KCl, and probed on a Western blot for kinesin and dynein, as well as for CPEB. For reciprocal immunoprecipitation experiments, the extract from CPEB-myc13-infected neurons was incubated with monoclonal antibodies against cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain or kinesin heavy chain; mouse IgG served as a negative control. The immunoblots were probed with antibodies against CPEB-myc13, dynein, and kinesin. The asterisk denotes the breakdown product of CPEB-myc13.