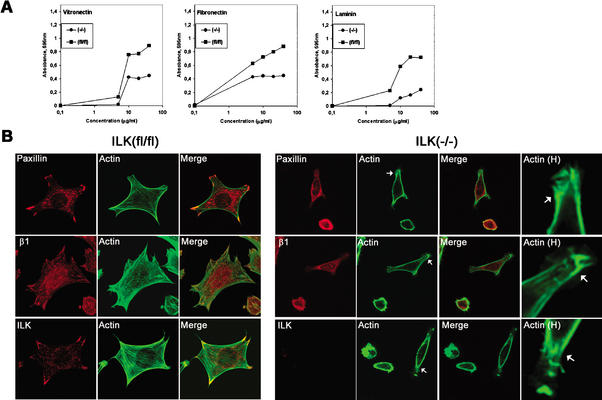
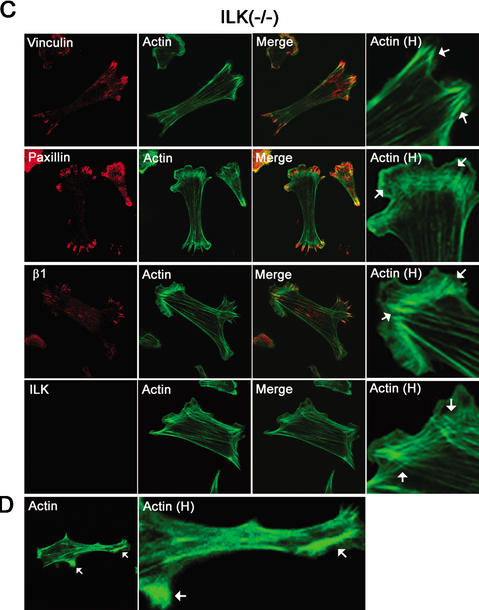
Figure 6.
Effect of ILK deletion on adhesion of fibroblasts. (A) Cell adhesion of ILK-floxed (fl/fl) and ILK-deficient (−/−) cells on vitronectin, fibronectin, and laminin-1. Attachment activity was quantified by spectrophotometric analysis at OD = 595 nm after staining of adherent cells with crystal violet. (B) Double immunostaining of ILK-floxed (fl/fl) and ILK-deficient (−/−) cells for paxillin/F-actin, β1-integrin/F-actin, and ILK/F-actin 4 h after adhesion to fibronectin. Note the reduced spreading and the lack of FA formation. Panels labeled Actin H show F-actin localized to subcortical areas where it formed large aggregates (arrows). (C) Double immunostaining of ILK-deficient (−/−) cells with vinculin/F-actin, paxillin/F-actin, β1-integrin/F-actin, and ILK/F-actin 16 h after adhesion to fibronectin. ILK-deficient cells were less spread but formed stress fibers and FAs. Aggregates of actin were still present. Panels labeled Actin H are higher-magnification views showing the increase of F-actin at focal adhesion (arrows). (D) F-Actin aggregates in subcortical areas (arrows; higher-magnification view is shown in panels labeled Actin H).