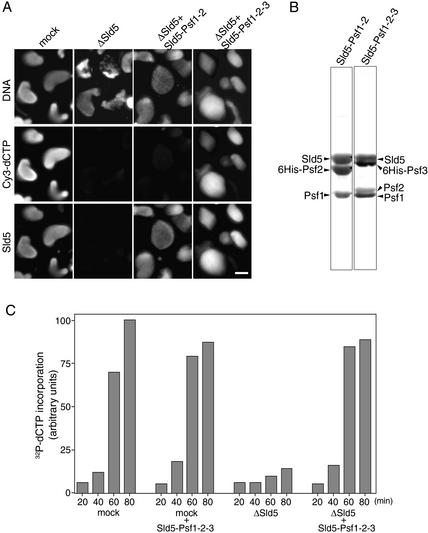
Figure 3.
Requirement of GINS for DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts. (A) Immunofluorescent detection of nuclear Sld5. Xenopus sperm chromatin was incubated in the presence of Cy3-dCTP in mock- or Sld5-depleted extracts supplemented with or without recombinant Sld5–Psf1–Psf2 or Sld5–Psf1–Psf2–Psf3 (GINS). After incubation at 23°C for 45 min, samples were fixed and centrifuged through 30% sucrose onto coverslips. Nuclear localization of Sld5 was visualized with rabbit anti-Xenopus-Sld5 antibody followed by Alexa488-labeled anti-rabbit IgG. DNA replication was monitored as the incorporation of Cy3-dCTP into DNA, and DNA was visualized with Hoechst 33258 dye. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Protein compositions of recombinant Xenopus Sld5–Psf1–Psf2 and Sld5–Psf1–Psf2–Psf3 complexes. Xenopus Sld5, Psf1, and Psf2 were coexpressed with and without Psf3 (either Psf2 or Psf3 was tagged with His6) in Sf9 cells using a baculovirus expression system. The protein complexes, purified with Ni-NTA resin, were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Ponceau S. (C) Replication activities of Sld5-depleted extracts. Xenopus sperm chromatin was incubated in mock- or Sld5-depleted extracts in the presence of 32P-labeled dCTP, supplemented with or without recombinant GINS. At the indicated times, DNA was isolated and subjected to alkali agarose gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography. The amount of 32P incorporated into DNA was quantified and expressed in arbitrary units.