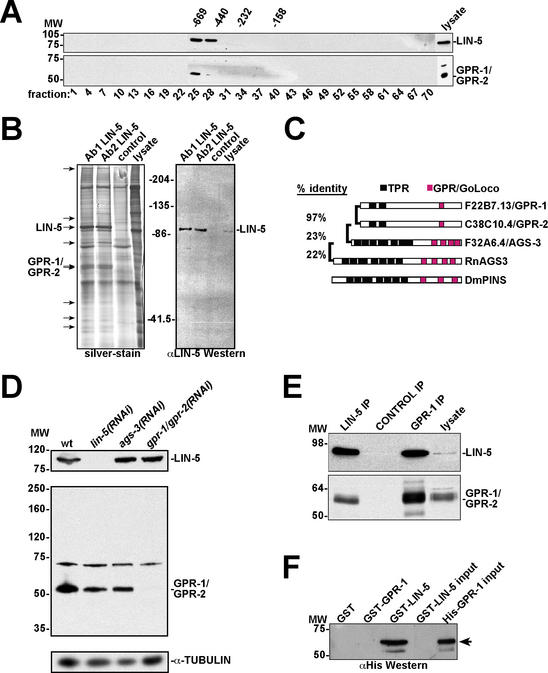
Figure 1.
A LIN-5 protein complex contains the GoLoco/GPR motif proteins GPR-1 and GPR-2. (A) Anti-LIN-5 (top panel) and anti-GPR-1 (bottom panel) Western blots of gel filtration chromatography fractions from C. elegans embryo lysates. LIN-5 and GPR-1/GPR-2 coelute in the early fractions. Numbers above panels are molecular weight markers in kilodaltons. Numbers below panels refer to fraction number. (B) Large-scale immunoprecipitation of LIN-5 for identification of interacting proteins. (Left) Silver-stained gel containing two LIN-5 IPs, the control (SD15 mAb) IP lane, and 50 μg lysate as indicated. Arrows point to protein bands in the LIN-5 IP lanes not observed in the control lane. Using tandem mass spectrometry, the ∼90-kD protein was identified as LIN-5 and the ∼60-kD doublet as GPR-1 and/or GPR-2. (Right) LIN-5 detected by immunoblotting, using 10% of the IPs. (C) Comparison between GPR-1, GPR-2, and other proteins containing TPR and GoLoco/GPR motifs. Rn, Rattus norvegicus; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster. C. elegans proteins are identified by their open reading frame designations and genetic names. (D) Anti-GPR antibody reactivity and specific elimination by RNAi. Western blots of RNAi embryo lysates using antibodies recognizing LIN-5 (top), GPR-1/GPR-2 (middle), and α-tubulin (loading control, bottom). (E) IP-Western blot demonstrating coprecipitation of LIN-5 and GPR-1/GPR-2 from C. elegans lysate. Antibodies indicated above the lanes were used in IPs followed by immunoblotting with anti-LIN-5 (top) and anti-GPR (bottom) antibodies. Input lysate (5%) was loaded on the right. (F) LIN-5 and GPR-1 interact directly in vitro. GST pulldowns with indicated proteins followed by immunoblotting with anti-His epitope antibody. GST-LIN-5 and His-GPR-1 input (5%) are loaded on the right.