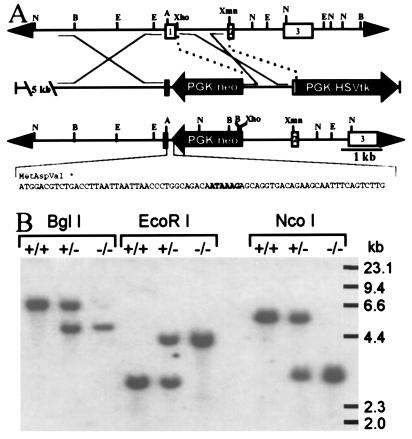
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse αA gene. (A) Strategy used to disrupt the αA gene. (Top) Normal αA locus. (Middle) Targeting vector. (Bottom) Disrupted αA locus. The sequence of an oligonucleotide inserted between the 5′ αA sequences and PGK/neo containing multiple stop codons in all three reading frames and a polyadenylylation signal (enclosed in box) is shown beneath a diagram of the targeted allele. Depicted restriction sites include NcoI (N), BglI (B), EcoRI (E), AatII (A), XhoI, and XmnI. HSVtk, herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) αA knockout mice. Liver DNA (15 μg) digested with BglI, EcoRI, and NcoI was hybridized with an XmnI/XhoI restriction fragment encompassing most of the first intron and the beginning of exon 2 (see A).