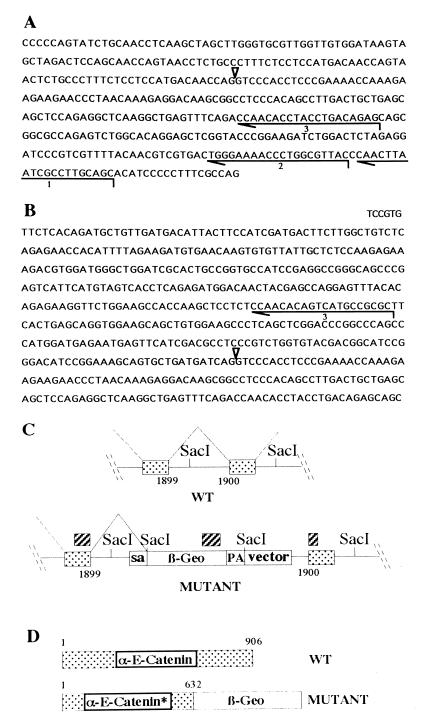
Figure 1.
Characterization of the gene trap vector insertion into the α-E-catenin locus. (A) Sequence of the gene trap vector around the splice acceptor site, which is indicated by an arrowhead. Lines 1, 2, and 3 show the primers used for cDNA synthesis, first and second PCR amplification rounds, respectively. (B) Sequence obtained by 5′ RACE from total RNA isolated from α-E-cateninGT1 heterozygous ES cells. Note the truncation of the vector sequence at exactly the splice acceptor site. The new sequence incorporated by splicing ends at the nucleotide number 1899 of the α-E-catenin coding region. (C) Structure of the insertion obtained. The hatched boxes indicate the 5′, internal, and 3′ probes used to characterize the insertion site. The SacI sites are represented to show the restriction fragment polymorphism used to identify the mutant allele. (D) Predicted structure of the mutant fusion protein produced. sa, Splice acceptor; pa, polyadenilation signal; WT, wild type.