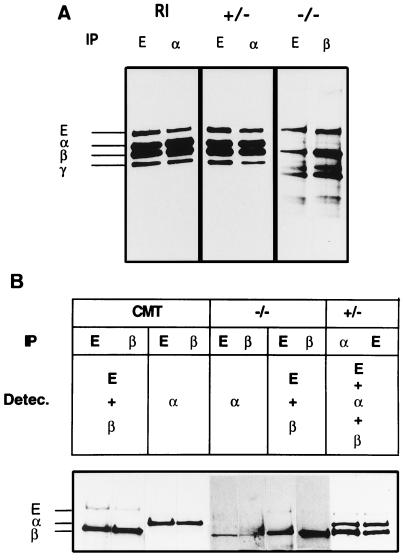
Figure 5.
Identification of the components of the cadherin–catenin complex in wild-type and mutant ES cells. (A) Cell lysates of metabolically labeled R1 (parental ES cell line), α-E-cateninGT1 heterozygous (+/−) and α-E-cateninGT1 homozygous (−/−) cells were precipitated with anti-E-cadherin, β- or α-catenin, as shown. Fluographs from R1 and heterozygous cells were exposed for 24 h, and those from homozygous mutant cells required 14 days exposure to detect a similar signal for E-cadherin and β-catenin. The positions of E-cadherin, α-catenin, β-catenin, and plakoglobin are shown on the left. (B) Cell lysates from CMT, −/− ES, and +/− ES cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-E-cadherin, β-catenin, or α-catenin antibodies as shown. Subsequently blots were subjected to ECL-detection with different combinations of the three antibodies, as shown. Again, the lanes corresponding to the homozygous mutant cells were overexposed to detect E-cadherin and β-catenin. Lanes 5 and 6 show a background band at the level of the β-catenin. This band is unspecific and appears as well in overexposures of CMT cells (lanes 3 and 4,and data not shown). The positions of the components of the complex are indicated on the left.