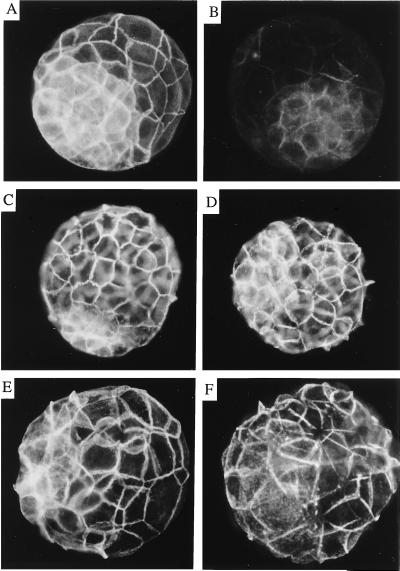
Figure 6.
Immunofluorescent detection of the components of the cadherin–catenin complex in mutant blastocysts. Blastocysts showing normal development (A, C, and E) and blastocysts showing a mutant phenotype (B, D, and F) were incubated with anti-α-catenin primary antibody and a fluorescein-conjugated secondary antibody. Normally developing embryos were positive for α-E-catenin, and embryos showing the mutant phenotype were negative or showed residual staining for α-E-catenin. Examples of a normal embryo showing a positive signal and a mutant embryo showing residual staining are shown in A and B, respectively. The photograph in B was exposed three times longer than photograph in A to show the residual staining. Mutant and wild-type embryos were then incubated with anti-E-cadherin (C and D) or anti-β-catenin (E and F) and a Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody.