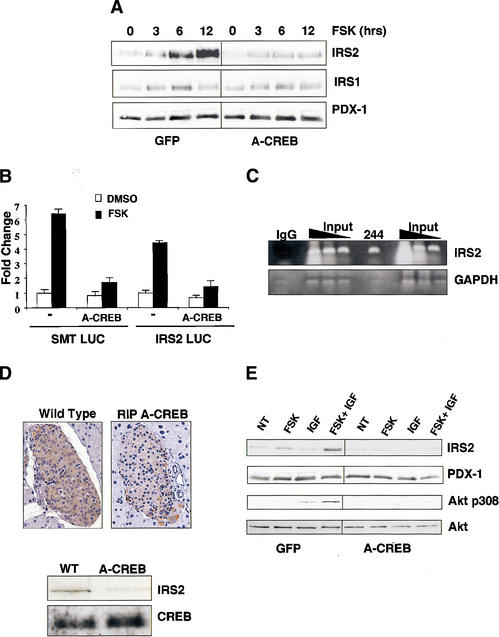
Figure 4.
CREB promotes insulin/IGF signaling via induction of IRS2. (A) Western blot analysis of IRS1 and IRS2 levels in MIN-6 cells treated with forskolin for increasing times in serum-supplemented medium. Cells were infected with A-CREB or control GFP adenovirus as indicated. (B) Transient transfection assay of 293T cells with IRS2 promoter construct or control somatostatin CRE luciferase plasmid. Cells treated with forskolin or DMSO vehicle. Cotransfection with A-CREB expression plasmid is indicated. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay of the IRS2 promoter using CREB 244 antiserum. Presence of the IRS2 promoter or negative control GAPDH in CREB immunoprecipitates determined by PCR amplification of anti-CREB or control IgG immunoprecipitates. (D) IRS2 expression is disrupted in A-CREB transgenic mice. (Top) Immunohistochemical staining of pancreatic sections from wild-type and RIP A-CREB transgenic mice using anti-IRS2 antiserum. (Bottom) Western blot assay of islet-cell extracts from wild-type and A-CREB mice using anti-IRS2 antiserum. Comparable levels of CREB protein in transgenic and wild-type lysates. (E) cAMP-dependent induction of IRS-2 potentiates growth factor signaling to Akt. Effect of IGF1 on Akt phosphorylation at Thr 308 in cells pretreated with forskolin or vehicle under serum-starved conditions for 8 h. Effect of A-CREB on IGF-stimulated Akt Thr 308 phosphorylation.