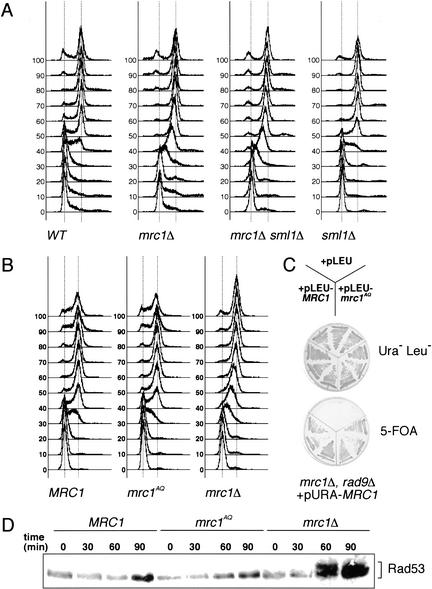
Figure 3.
mrc1AQ is competent for DNA replication. (A) The defect of Mrc1 during S phase is not suppressed by deleting SML1. Wild-type (WT; Y2305), mrc1Δ (Y2306), mrc1Δ sml1Δ (Y2307), and sml1Δ (Y2308) cells were arrested in G1 with α-factor and released into YPD at 30°C. Samples were removed at the indicated times and subjected to FACS analysis. The first and second broken vertical lines in each profile represent the 1n and 2n peaks of DNA content, respectively. (B) mrc1AQ mutants undergo a normal S phase. mrc1Δ (Y1127) cells carrying MRC1 (pMRC1), mrc1AQ (pAO138), or vector alone (pRS416) were arrested in G1 with α-factor and released into normal YPD at 30°C. Samples were removed at the indicated times and subjected to FACS analysis. The broken lines represent the peaks of DNA content as in A. (C) mrc1AQ mutants can suppress the lethality of mrc1Δ rad9Δ mutants. mrc1Δ rad9Δ cells carrying MRC1 on a URA3 vector (Y2297) were transformed with MRC1 (pAO122), mrc1AQ (pAO139), or empty LEU2 (pRS416) vectors. The strains containing both URA3 and LEU2 vectors were struck onto 5-FOA plates to select for cells that lost the MRC1-containing URA3 vector. Growth of the strains on plates selecting for both plasmids is shown as a control for the effect of the LEU2 plasmid on viability. (D) mrc1AQ mutants do not induce DNA damage during S phase. The strains used in B were arrested in G1 with α-factor and released into YPD at 30°C. Samples were removed at the indicated times, and Rad53 activation was assessed by mobility shift on a Western blot.