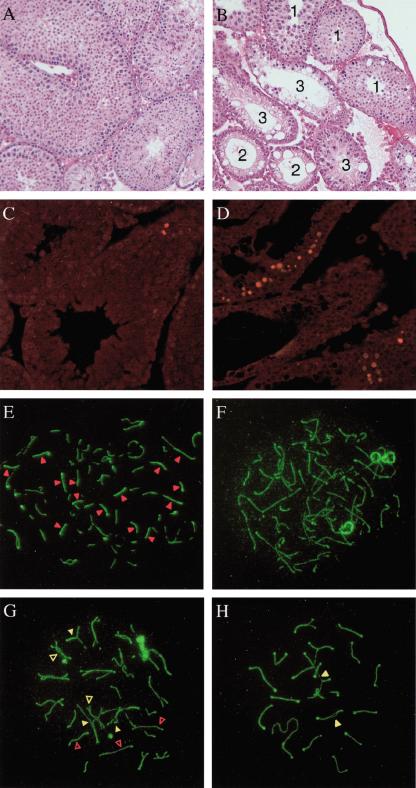
Figure 2.
Germ-cell and meiotic pairing abnormalities in Fancd2–/– mice. (A,B) H&E staining of testis sections from 7-week-old wild-type (A) or Fancd2–/– (B) littermates. All stages of spermatogenesis are seen in the wild-type adult testes. Fancd2–/– testes show a mosaic pattern of normal-appearing tubules (tubule 1), tubules with vacuolated Sertoli cell cytoplasm and no germ cells (tubule 2) and tubules with vacuolated Sertoli cell cytoplasm and decreased numbers of spermatocytes and spermatids (tubule 3). Magnification, 20×. (C,D) TUNEL staining of testes sections from 7-week-old wild-type (C) and Fancd2–/– (D) littermates. Occasional cells were labeled in wild-type tubules near the basement membrane, whereas Fancd2–/– testes contain tubules with multiple numbers of apoptotic spermatocytes. The nuclei of apoptotic cells are TUNEL-labeled with Cy3-dCTP and fluoresce red. Magnification, 20×. (E–H) Meiotic pairing abnormalities in Fancd2–/– spermatocytes detected by indirect immunofluorescence staining for Scp3 (green) and Rad51 (red). (E) Zygotene wild-type nucleus. (F) Zygotene Fancd2–/– nucleus with unusually long unpaired axial elements. (G) Late zygotene Fancd2–/– nucleus with multiple synaptic abnormalities. (H) Pachytene Fancd2–/– nucleus with unpaired (open arrowheads) and mispaired homologs (closed arrowheads). Magnification, 100×.