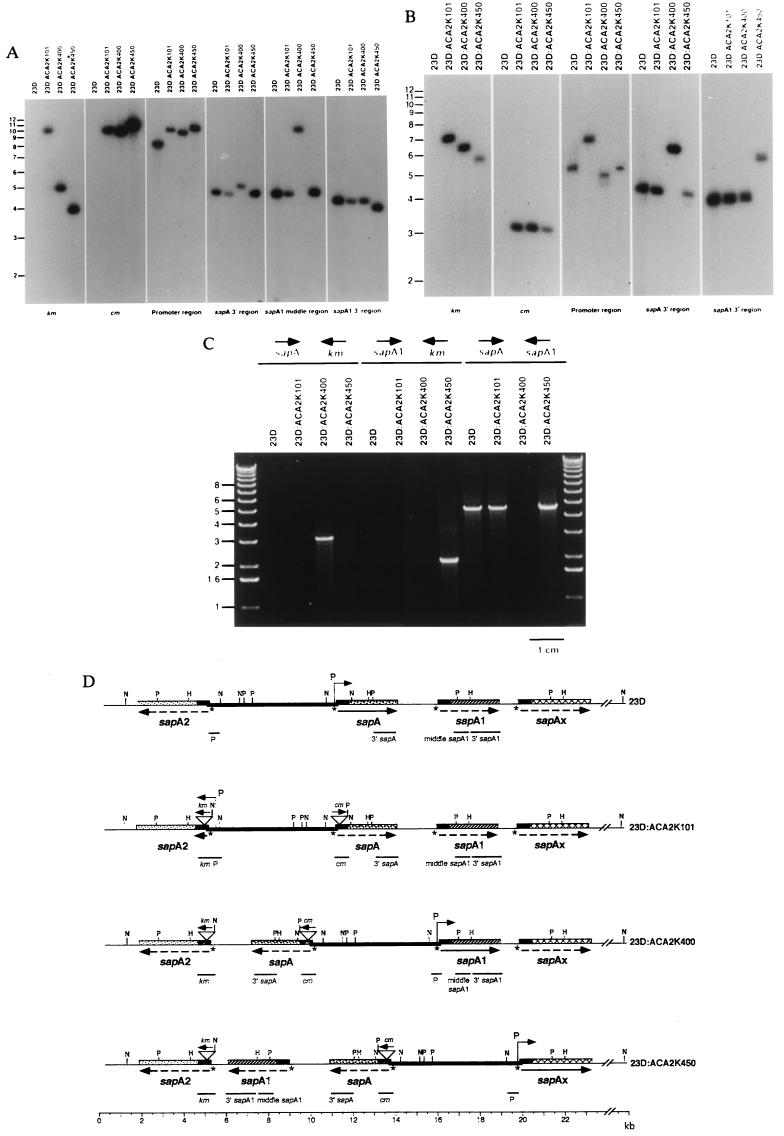
Figure 2.
Southern hybridization of HincII (A) or PstI (B) digestions of chromosomal DNA from C. fetus 23D and ACA2K series mutants using probes to km, cm, the promoter region, the sapA-specific 3′ region, the sapA1-middle region, or the sapA1-specific 3′ region. Each probe hybridized to a single fragment regardless of the phenotype of the C. fetus strain. (C) Mapping of SLP gene cassette arrangement by PCR. PCRs were performed with template chromosomal DNA from strains 23D and ACA2K mutants using sapA-specific 3′ region forward (sapA) and km reverse (km) primers (left four lanes), sapA1-specific 3′ region forward (sapA1) and km primers (center four lanes), or sapA and sapA1-specific 3′ region reverse (sapA1) primers (right four lanes). (D) Cumulative restriction maps of the four strains presented in A–C. The location of the probes as indicated from the hybridizations is shown under the map for each strain. sapAx represents an uncharacterized SLP gene cassette; arrows represent the direction of transcription; solid lines represent expressed genes, dashed lines represent silent genes; P over bent arrows represents the sapA promoter; and the heavy line represents the 6.2-kb invertible promoter-containing element, flanked by opposing SLP gene cassettes. The asterisks represent the palindromic putative recombinase recognition sites (TTAAGGAaTCCTTAA) present in the 5′ conserved region of each SLP gene cassette (7), and restriction sites are indicated: H, HincII; N, NdeI; P, PstI.