Fig. 1.
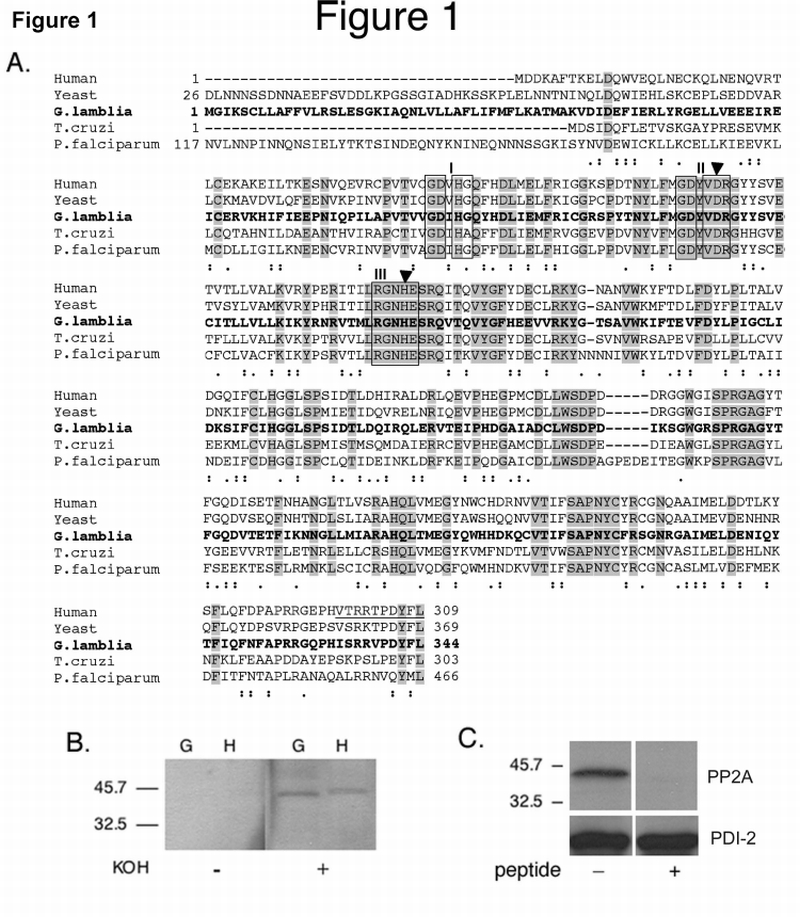
Amino acid sequence homology comparison between Giardia and other PP2A‐C subunits, evidence for L‐methylation of Giardia PP2A‐C and control for anti‐PP2A‐C antibody specificity.
A. Amino acid sequence alignment of human PP2A‐C (GenBank Accession no. P62714), yeast, (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, GenBank Accession no. P23594), Giardia (GenBank Accession no. XP_767901), Trypanosoma cruzi (GenBank Accession no. AAO17777.1) and Plasmodium falciparum (GenBank Accession no. AAC47800.1) PP2A‐C subunits. Identical and semi‐conserved amino acids are shaded shown with dots, respectively. The highly conserved phosphoesterase domains I, II, and III are boxed. The filled triangles show the conserved histidine and aspartate residues, which act as an ion‐pair in catalysis. The underlined peptide indicates the sequence used to generate the polyclonal Ab299/309.
B. Methylation of gPP2A‐C: Western blot of total lysates of vegetative Giardia trophozoites (G) and HT‐29 cells (H). Prior to reacting with the methylation sensitive polyclonal Ab299/309, the membrane was treated with 0.2M KOH (+) to remove methyl groups or with PBS (−). Demethylation of both giardial and human PP2A‐C proteins is necessary for antibody reactivity.
C. Antibody specificity: Western blot of total cell lysates of vegetative Giardia trophozoites in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the Giardia specific peptide. Competition with the gPP2A‐C C‐terminal peptide ‘HISRRVPDYFL’ inhibited all binding of the anti‐PP2A‐C antibody to gPP2A‐C.
