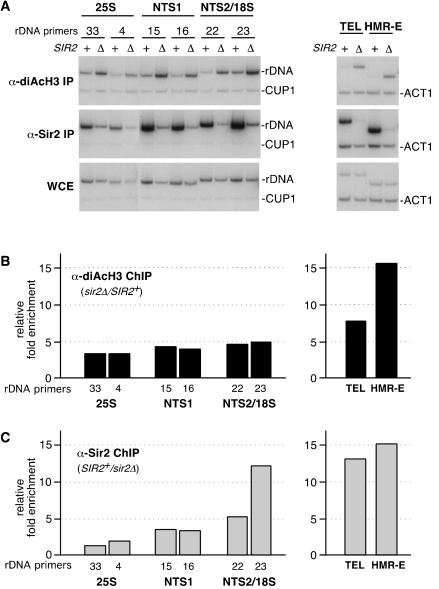
Figure 2.
H3 acetylation levels throughout rDNA are increased in sir2Δ cells. (A) Examples of the ChIP data used to determine the associations of diacetylated (K9/K14) histone H3 or Sir2 with rDNA (left panels) or telomeric (TEL) and mating-type loci (HMR-E) regions (right panels). (+) SIR2+ cells; (Δ) sir2Δ cells; numbers above the left panels refer to rDNA primers as indicated in Figure 1A. CUP1 and ACT1 primers were used as internal controls. (B, left) Quantification of ChIP experiments shows that the relative fold enrichment of diacetylated H3 increases throughout the rDNA in sir2Δ cells as compared with SIR2+ cells. rDNA primers are indicated below the graph and correspond to Figure 1A. (Right) H3 acetylation increases at telomeres and the silent mating-type loci in sir2Δ cells. (C, left) Association of Sir2 with rDNA in SIR2+ and sir2Δ cells showing that the highest levels of Sir2 are present at NTS1 and NTS2/18S. (Right) Association of Sir2 with telomeres and the silent mating-type loci is shown for comparison.