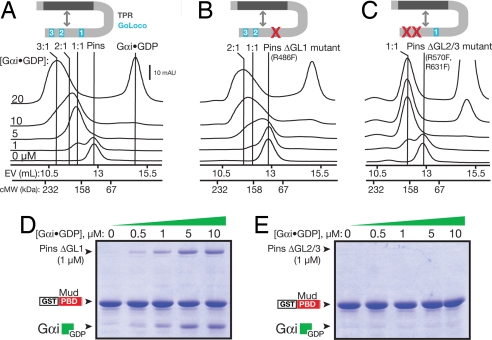
Fig. 2.
Differential repression of the three GoLocos by the Pins intramolecular interaction. (A) Analysis of Pins binding to Gαi·GDP by gel-filtration chromatography. Pins and mixtures of Pins and Gαi·GDP were separated by gel filtration. Marks indicating the elution volumes of 2:1 and 1:1 Gαi:Pins complexes were determined by using single and double Pins GoLoco mutants, respectively. The column elution volumes (EV) of standard proteins to give a calibrated molecular weight (cMW) are shown on the x axis. The protein composition of the 20 μM Gαi eluate for this and B and C are shown in SI Fig. 5C. (B) Analysis of Pins with an inactive GoLoco1 (Pins ΔGL1) binding to Gαi·GDP by gel-filtration chromatography. Loss of GoLoco1 causes loss of the high-affinity peak that occurs at low Gαi concentrations. (C) Analysis of Pins with an inactive GoLoco 2 and 3 (Pins ΔGL2/3) binding to Gαi·GDP by gel-filtration chromatography. Only the high-affinity interaction remains after loss of GoLocos 2 and 3. (D) Cooperative binding of Gαi and Mud to Pins does not require GoLoco1. In the absence of GoLoco1, Gαi·GDP enhances the affinity of Pins for Mud. (E) GoLocos 2 and 3 are required for cooperative binding of Gαi and Mud to Pins. Although Gαi·GDP can bind to Pins in which GoLocos 2 and 3 are inactivated (C), binding does not lead to cooperative Mud binding.