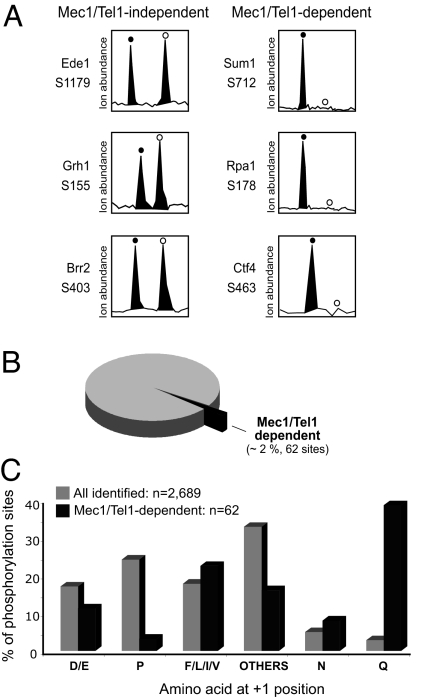
Fig. 2.
Identification and analysis of Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphorylation. (A) Relative ion abundances of selected phosphopeptides (with the indicated phosphorylation site) in WT (filled circles) and mec1Δ tel1Δ (open circles) cells. (Left) Example of phosphopeptides present at similar abundance in both cells, thereby containing a Mec1/Tel1-independent phosphorylation. (Right) Example of phosphopeptides specifically present in wild-type cells, thereby containing a Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphorylation. For these Mec1/Tel-dependent phosphorylations, the open circles indicate the expected position of the phosphopeptide ions from mec1Δ tel1Δ cells (labeled with d10-Nisotag). (B) Number and percentage of Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphorylation identified relative to the total number of phosphorylation sites identified (2,689 phosphorylation sites and 1,109 proteins; see Methods for detailed description of criteria used). (C) Comparison of the frequency of amino acids at the +1 position of phosphorylated serine or threonine for all identified phosphorylation (gray bars) and Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphorylation (black bars).