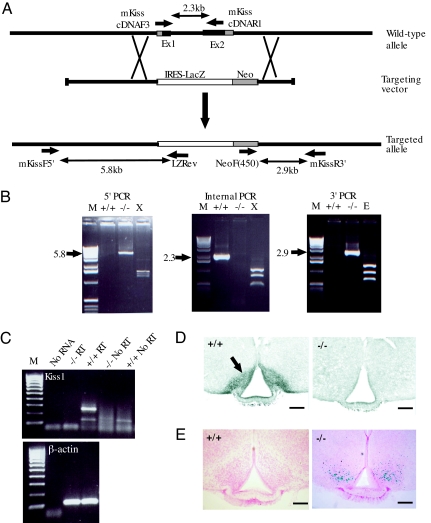
Fig. 1.
Kiss1 gene targeting. (A) Gene targeting strategy. Kiss1 exons are indicated as shaded boxes with the coding sequence in black. The targeting vector replaces the complete Kiss1 coding region with an IRES-LacZ sequence. The location of primers used to confirm the correct targeting event and loss of Kiss1 coding sequence in the mutant mice are shown along with the size of the PCR products. (B) PCR analysis of Kiss1 locus in mutant mice. The identity of the PCR products was confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion. X, XcmI; E, EcoRI; M, Invitrogen 1-kb DNA marker. (C) RT-PCR of Kiss1gene expression confirming the null allele. (D) Immunohistochemical detection of KISS1 neurons in the ARC of the hypothalamus. (Scale bars: 300 μm.) (E) β-galactosidase activity in the ARC of mutant mice. (Scale bars: 300 μm.)