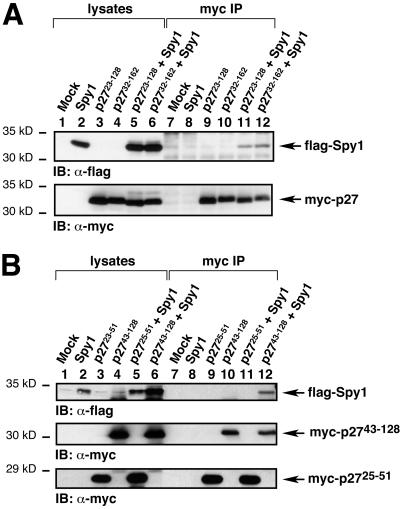
Figure 2.
Spy1 interacts in vivo with the mouse p27 clones isolated from the two-hybrid screen. (A) 293T cells were transiently transfected with the indicated constructs, lysed, immunoprecipitated with α-myc sera, analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE, and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was then immunoblotted with α-flag sera to detect flag-tagged Spy1 (top panel). As shown in lanes 11 and 12 of the top panel, flag-Spy1 coimmunoprecipitates with myc-p2723–128 and myc-p2732–162, respectively. The membrane was then stripped and reprobed with α-myc sera to demonstrate the presence of the myc-tagged p27 constructs (bottom panel). (B) 293T cells were transfected with the indicated constructs, lysed, immunoprecipitated with α-myc sera, and analyzed as above. Myc-p27 25–51, which is the cyclin-binding region of p27, did not appear to bind to flag-Spy1 (lane 11). In contrast, myc-p27 43–128, which encompasses the CDK-binding region of p27, interacted with flag-Spy1 (lane 12).