Figure 2.
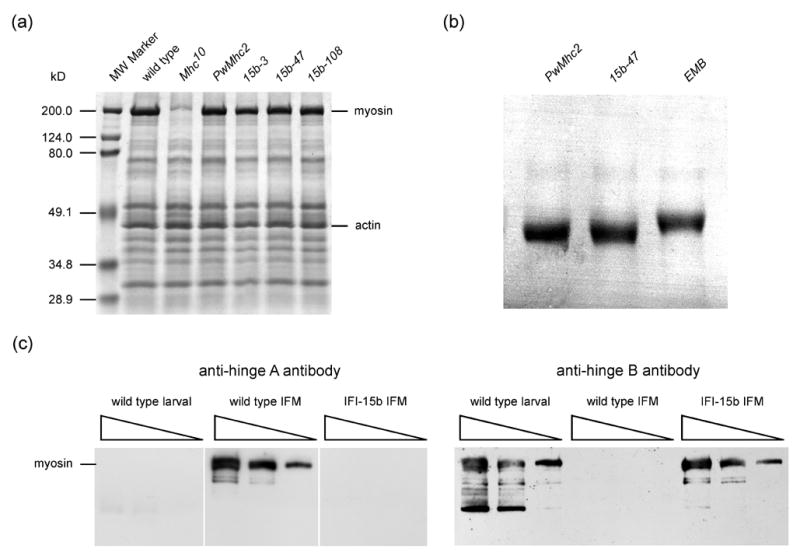
Expression of myosin in the IFI-15b hinge-switch transgenic lines. (a) 10% SDS-PAGE analysis of proteins from the upper thorax of wild-type (yw), Mhc10 (IFM/TDT MHC-null line), PwMhc2 (transgenic control) and each of the high expressing hinge-switch lines, indicated as 15b-3, 15b-47, and 15b-108, in the Mhc10 genetic background. MHC level relative to actin level was designated as 100% for wild type and found to be 99.7 ± 3.7 (n = 11) for PwMhc2, 99.9 ± 2.2 (10) for 15b-3, 107.0 ± 5.3 (6) for 15b-47, and 102.3 ± 4.7 (6) for 15b-108. Mean value ± SEM is reported. (b) IFM MHC from PwMhc2 control, 15b-47 (IFI-15b), and EMB fly lines, all in the Mhc10 genetic background. Proteins were loaded on a 5% SDS-polyacrylamide (1% bis-acrylamide) mini-gel. Samples were subjected to prolonged electrophoresis for 5 hours at a constant current of 25 mA to resolve migration differences resulting from primary sequence variation in the MHC isoforms. EMB flies express a transgenic embryonic MHC isoform32, in which the C-terminal tailpiece is 26 residues longer than the wild-type indirect flight muscle or IFI-15b isoforms. EMB MHC therefore has a lower mobility through the gel matrix. MHC from both PwMhc2 and 15b-47 IFM appear to have similar molecular masses and higher mobilities than EMB MHC. (c) Immunoblots of whole wild-type (yw) larvae, wild-type (yw) IFM and IFI-15b-expressing (15b-3) IFM in the Mhc10 genetic background, probed with either a hinge A- or hinge B-specific polyclonal antibody. Three different volumes of each sample were loaded into neighboring lanes on the gel. The hinge A-specific antibody recognized MHC from wild-type IFM and failed to recognize larval MHC or an MHC isoform in hinge-switch IFM (all samples were from the same gel and blot). Conversely, the hinge B-specific antibody recognized larval MHC and MHC expressed in hinge-switch fly IFM, but not MHC from wild-type IFM. Bands migrating faster than myosin are likely to be proteolytic products that are more readily detected on immunoblots due to their high efficiency transfer relative to full-length MHC. However, the identity of a major low molecular weight larval band is unknown.
