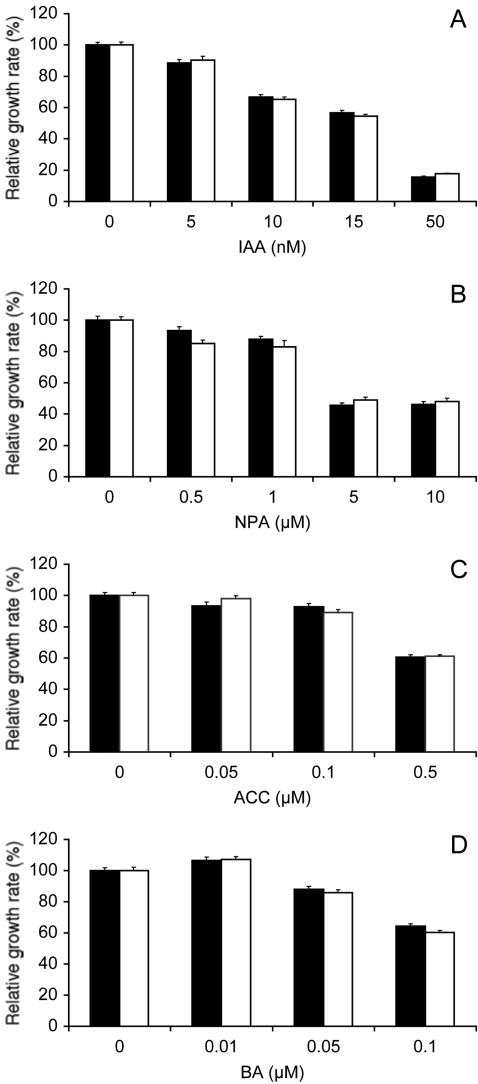
Figure 3.
Root growth sensitivity to phytohormones and a polar auxin transport inhibitor. A to D, Relative root growth rate of wild-type Est (black bars) and arl2-1 mutant seedlings (white bars) in the presence of varying concentrations of IAA (A), naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA; B), 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC; C), or N6-benzyladenine (BA; D). Four-day-old seedlings were transferred onto fresh germination medium (GM) containing 0.1% (v/v) ethanol (A and D), 0.05% (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide (B), or 0.05% (v/v) isopropanol (C) with the indicated concentrations of IAA, NPA, ACC, or BA. Root growth was measured over a period of 2 d. Average root growth rates were determined for each compound concentration and divided by the corresponding growth rate in absence of the compound (control). ses are represented by vertical bars. The numbers of seedlings tested in these experiments were 36 to 52 (A), 27 to 43 (B), 44 to 91 (C), and 81 to 95 (D). Average growth rates in the absence of added compounds were: A, 5.2 ± 0.09 (Est) and 4.5 ± 0.08 (arl2-1) mm d-1; B, 4.6 ± 0.12 (Est) and 4.5 ± 0.12 (arl2-1) mm d-1; C, 4.4 ± 0.09 (Est) and 5.09 ± 0.1 (arl2-1) mm d-1; and D, 5.2 ± 0.09 (Est) and 5.0 ± 0.1 (arl2-1) mm d-1.